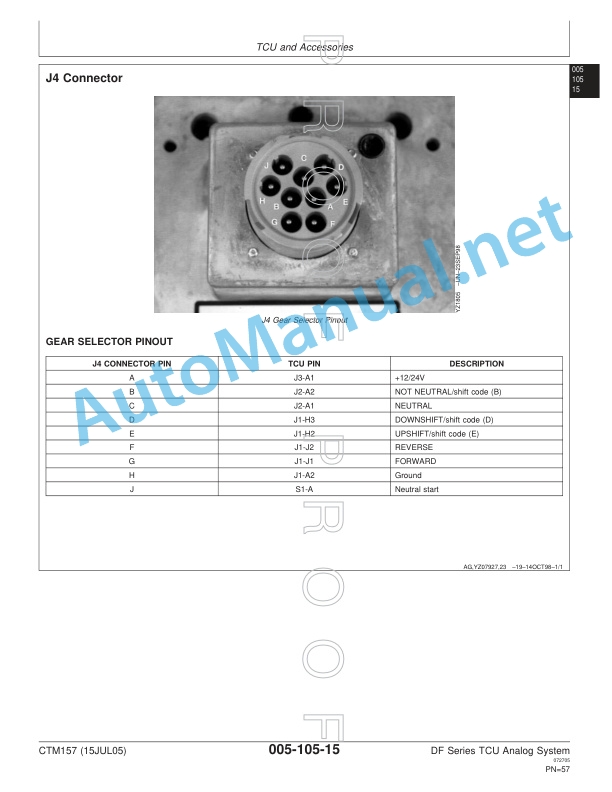
Claas Celtis 456-426 Rx, Rc, Ra (A07) Tractors Operator Manual EN
$50.00
- Model: Celtis 456-426 Rx, Rc, Ra (A07) Tractors
- Type Of Manual: Operator Manual
- Language: EN
- Format: PDF(s)
- Size: 29.8 MB
File List:
00 0301 051 0.pdf
00 0303 482 0.pdf
00 1116 871 0.pdf
00 1132 312 0.pdf
00 1169 984 0.pdf
00 0301 051 0.pdf:
PROFI CAM 3
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Notes on the manual
1.1.1 Validity of manual
1.1.2 Information about this Operator’s Manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.1.4 Optional equipment
1.1.5 Qualified specialist workshop
1.1.6 Maintenance information
1.1.7 Warranty notes
1.1.8 Spare parts and technical questions
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Intended use
1.2.2 Reasonably foreseeable misuse
2 Safety
2.1 Identifying warnings
2.1.1 Hazard signs
2.1.2 Signal word
2.2 Safety rules
2.2.1 Meaning of Operator’s Manual
2.2.2 Observing safety decals and warnings
2.2.3 Optional equipment and spare parts
3 Product description
3.1 Overview and method of operation
3.1.1 How the PROFI CAM works
3.2 Identification plates and identification number
3.2.1 Position of identification plates
3.2.2 Explanation of PROFI CAM identification plate
3.3 Information on the product
3.3.1 CE marking
4 Operating and control elements
4.1 Camera system
4.1.1 Camera system monitor
4.2 Menu structure
4.2.1 Main menu
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5
4.2.6
5 Technical specifications
5.1 PROFI CAM
5.1.1 Monitor
5.1.2 Camera
5.1.3 Switch box
5.1.4 Degree of protection against foreign bodies and water
6 Preparing the product
6.1 Shutting down and securing the machine
6.1.1 Switching off and securing the machine
6.2 Prior to operation
6.2.1 Carry out prior to operation
6.2.2 Installing the sun protection
6.2.3 Aligning the camera
6.2.4 Connecting the camera electrics
7 Operation
7.1 Monitor
7.1.1 Switching on the monitor
7.1.2 Calling up the menu
7.1.3 Setting a menu item
7.1.4 Setting the image orientation
7.1.5 Setting automatic screen darkening
7.1.6 Image mirroring
7.1.7 Setting the trigger view
7.1.8 Setting the follow-up time for trigger view
7.1.9 Setting the display mode
7.1.10 Activating/deactivating a display mode
8 Faults and remedies
8.1 Electrical and electronic system
8.1.1 Overview of problems on PROFI CAM camera system
8.1.2 Replacing the switch box fuse
9 Maintenance
9.1 Maintenance intervals
9.1.1 Every 10 operating hours or daily
9.2 Camera system
9.2.1 Checking the camera system for dirt
9.2.2 Cleaning the camera
9.2.3 Cleaning the switch box
9.2.4 Cleaning the monitor
10 Placing out of operation and disposal
10.1 General Information
10.1.1 Putting out of operation and disposal
11 Technical terms and abbreviations
11.1 Abbreviations
11.1.1 Units
11.1.2 Abbreviations
11.1.3 Technical terms
00 0303 482 0.pdf:
PROFI CAM 4
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Notes on the manual
1.1.1 Validity of manual
1.1.2 Information about this Operator’s Manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.1.4 Optional equipment
1.1.5 Qualified specialist workshop
1.1.6 Maintenance information
1.1.7 Notes on warranty
1.1.8 Spare parts and technical questions
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Intended use
1.2.2 Reasonably foreseeable misuse
2 Safety
2.1 Identifying warnings
2.1.1 Hazard signs
2.1.2 Signal word
2.2 Safety rules
2.2.1 Meaning of Operator’s Manual
2.2.2 Structural changes
2.2.3 Optional equipment and spare parts
2.2.4 Operation only following proper putting into operation
2.2.5 Technical status
2.2.6 Respecting technical limit values
Respecting technical limit values
2.2.7 Hazards when driving on roads and fields
3 Product description
3.1 Overview and method of operation
3.1.1 How the PROFI CAM works
3.2 Identification plates and identification number
3.2.1 Identification plates
3.3 Information on the product
3.3.1 CE marking
4 Operating and display elements
4.1 Camera system
4.1.1 Camera system monitor
4.1.2 CEBIS
4.2 Menu structure
4.2.1 Main menu
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5
4.2.6
5 Technical specifications
5.1 PROFI CAM
5.1.1 Monitor
5.1.2 Camera
5.1.3 Switch box
6 Preparing the product
6.1 Switching off and securing the machine
6.1.1 Switching off and securing the machine
6.2 Prior to putting into operation
6.2.1 Carry out prior to operation
6.2.2 Installing the sun protection
6.2.3 Aligning the camera
7 Operation
7.1 Monitor
7.1.1 Switching on the monitor
7.1.2 Calling up the menu
7.1.3 Setting a menu item
7.1.4 Setting the image orientation
7.1.5 Setting automatic screen darkening
7.1.6 Image mirroring
7.1.7 Setting the trigger view
7.1.8 Setting the follow-up time for trigger view
7.1.9 Setting the display mode
7.1.10 Activating/deactivating a display mode
8 Faults and remedies
8.1 Electric and electronic system
8.1.1 Overview of problems on PROFI CAM camera system
9 Maintenance
9.1 Maintenance intervals
9.1.1 Every 10 operating hours or daily
9.2 Camera system
9.2.1 Checking the camera system for dirt
9.2.2 Cleaning the camera
9.2.3 Cleaning the switch box
9.2.4 Cleaning the monitor
10 Putting out of operation and disposal
10.1 General information
10.1.1 Putting out of operation and disposal
11 Technical terms and abbreviations
11.1 Abbreviations
11.1.1 Units
11.1.2 Abbreviations
11.1.3 Technical terms
00 1116 871 0.pdf:
CONTENTS
For your safety
Warning triangle
Appropriate use
Chapter symbols
CHAP-C-GB.pdf
C – Electrical system (Cab)
CHARACTERISTICS
TOWING SOCKET
Trailer/implement light socket (A)
1 – Left direction indicators.
2 – Available.
3 – Earth.
4 – Right direction indicators.
5 – Right side lights + number plate light.
6 – Brake light.
7 – Left side lights.
Electric cabinet power socket (B)
Event counter connector (C) for the on-board computer
LIGHTING – INDICATORS
AT THE FRONT
1 – Main beam lights.
2 – Dipped headlights.
3 – Side indicator repeaters.
4 – Working lights.
5 – Rotating beacon.
6 – Dipped headlights (depending on equipment fitted and destination).
At the rear
7 – Side indicator repeaters:
8 – Plate lighting.
9 – Working lights.
10 – Reflector.
CONTROLS
Direction indicators
Horn (III)
Headlights
To flash headlights
Rotating beacon
Hazard warning lights
Working lights
Windscreen wiper
Screen washer
Tilting of dipped headlights
Overhead light (D)
A – Lighting turned on.
B – Lighting turned on.
C – Lighting turned off.
Key operated ignition
Key ignition positions
Allocation of fuses
Removable fuse
Battery master switch
Fuse box
C – Electrical system (Roll bar)
TOWING SOCKET
LIGHTING – INDICATORS
AT THE FRONT
1 – Main beam lights.
2 – Dipped headlights.
3 – Side indicator repeaters.
4 – Rear view mirrors.
5 – Rotating beacon.
At the rear
6 – Working headlight.
7 – Side indicator repeaters:
8 – Plate lighting.
9 – Trailer/implement light socket.
10 – Electric cabinet supply socket.
Trailer/implement light socket (9)
Electric cabinet power socket (10)
Fuse box
CHAP-D-GB.pdf
D – ENGINE
CHARACTERISTICS
Operations before start
STARTING THE ENGINE
A. COLD ENGINE
B. WARM ENGINE
Engine starting help when cold
FUEL HEATER
COOLANT HEATER
STOPPING THE ENGINE
OPERATION
RUNNING-IN
Recommendations:
1 – Avoid operating lightly loaded or for long periods at idle. Lack of load during the first 100 hours can cause glazing of the cylinder liners. This leads to excessive oil consumption and loss of power.
2 – Avoid overloading the engine: The engine suffers overload when too high a gear ratio is used and engine speed drops to about…
3 – Pay particular attention to fluid levels (oil and coolant) as well as engine temperature.
Operating temperature
OPERATING RPM
Maximum off-load rpm
Maximum speed on the road
Specific consumption
Operating at intermediate power
Full power operation
Quality requirement
Filling the tank
1 – Clean the area around the fuel filler cap.
2 – Remove the filler cap (1) and put it in a clean dry place.
3 – After refuelling, replace and tighten the filler cap.
Handling the fuel
Bleeding air from the injection system
CHAP-E-GB.pdf
E – Transmission
Revershift, Twinshift or hydraulic doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in the road range
Engine speed 2 300 rpm (Celtis 426, 436, 446)
Engine speed 2 200 rpm (Celtis 456)
Mechanical doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in road range
Engine speed 2 300 rpm (Celtis 426, 436, 446)
Engine speed 2 200 rpm (Celtis 456)
Without doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in road range
Engine speed 2 300 rpm (Celtis 426, 436, 446)
Engine speed 2 200 rpm (Celtis 456)
Tables of forward speeds
GEAR BOX
Mechanical drive reverser
I – Forward
II – Reverse
Electro-hydraulic drive inverter REVERSHIFT
I – Forward
II – Neutral
III – Reverse
IV – De-clutched
REVERSHIFT progressive inversion selector
Gear selection
Mechanical range doubler
Electro-hydraulic range doubler
Range selection
I – Reduced speed
II – Normal speed
Selection of the crawling speed
Differential
Brake system
Brake pedal (1)
Trailer brake
Hydraulic braking
Pneumatic brake
Handbrake
To apply the hand brake:
To release:
Power take-off with mechanical engagement
De-clutching
Hydraulically-engaged power take-off
Releasing and engaging the clutch
Selection of PTO speeds
Selection of a revolution speed
Procedure for setting off again
Hitching-up and towing PTO attachments
Imperative
Stationary working
1 Press (1).
2 Pull the chock towards you.
3 Locking lug.
Towing the tractor
CHAP-F-GB.pdf
F – Front axles – driven and undriven
CHARACTERISTICS
Front axle engagement
Operating mode
Choice of operating mode
Override mode
Automatic mode
Brake system
CHAP-G-GB.pdf
G – Hydraulics – rear linkage and hitch
Characteristics
Hydraulic pump (2 pumps with gears)
Fluid capacities
Hydraulic lift
Rear lift
Position control
Operation
Force control
Operation
Adjustment
Implement handling at end of row
Position control
Force control
Implement control using force control
Mixed control
Operation
Adjustment
Implement handling at end of row
Implement handling at end of row
Exterior control lever
Operation
Lowering the linkage
Raising the linkage
Lowering the linkage
Raising the linkage
Auxiliary spool valves
Control levers and pressure connectors
Control levers
Hydraulic coupler
Single-acting spool valve
Operation
Pressurising
Return to the tank
Dual effect distributor
Operation
Pressurising the yellow take-off point
Pressurising the red take-off point
Floating
Dual acting/single acting conversion
Distributor control cross lever
Operation
Pressurising the yellow take-off point
Pressurising the red take-off point
1 – Cross control totally locked.
2 – Distributor control (II) locked.
3 – No locking.
Flow regulator
Operation
Free return
Linkage (Electronic tracto control) TCE 9
Control panel
1 – 4-position memory knob.
2 – Shock absorber activator switch with associated light.
3 – Position setting instruction knob.
4 – Linkage safety mode and warning light.
5 – Upper limit adjustment selector.
6 – Linkage motion indicator lights (up/down).
7 – Control mode setting adjuster (force / position).
8 – Lowering speed adjustor.
Linkage operation conditions
Position control
Operation
Force control
Operation
Upper limit adjustment
Operation
Rate of descent adjustment
1 – Place switch (1) in the upper position .
2 – Select minimum lowering speed using button (8).
3 – Move switch (1) to the working position .
Function of the external control buttons
Operation
4-position memory button
High position
Transport lock
STOP position
Working position
Deep working
The travel shock absorber
Operation
Motion indicator warning light
Linkage emergency and safety warning light
Steady light
Flashing light
If the warning light is off after starting up
Instructions for adjusting the rear hitch
Influence of hitch geometry on lifting capacity
A – Top link (upper link attachment point with respect to the centre line of the wheels and the length of the link).
B – Lower links (lower link attachment points).
C – Lifting rods (length of lifting rods).
Maximum mechanical advantage
Minimum mechanical advantage
Adjusting the lifting rods
Adjustment of the upper rod
Adjustment
Adjusting the stabilisers
Adjustment
Self-locking stabiliser
Automatic hitching
Automatic hooks
Coupling the implement
Uncoupling the implement
Maintenance
Draw bar couplings
Automatic pick-up hitch
Coupling an implement
CHAP-H-GB.pdf
H – FRONT POWER TAKEOFF, LINKAGE AND FRONT COUPLING – Front loader
CHARACTERISTICS
FRONT LINKAGE
FRONT POWER TAKE-OFF
Front hitch
Front loader
Characteristics established at a pressure of 190 bar and at a rate of 60 litres/min
Data varies depending on type of tractor.
USING THE FRONT LINKAGE SYSTEM
Operation
Arm adjustment
Adjusting the top linkage
Front power take-off
Operation
Starting up
Frontal loader control
ACTIVATIONFrontal loader control
For the Propilot (1)
For the Flexpilot (2)
Operation
1st function
2nd function
3rd function
4th function
Unhitching of the frontal loader
Operation on left side
Operations on right side
Linkage of the frontal loader
Operations on right side
Operations on left side
Linkage of the tool
Unhitching of the tool
Level indicator
PCH system
Maintenance on the tractor with frontal loader
CHAP-I-GB.pdf
I – On board computer
On-board computer (INFOTRAC)
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION (cont)
POSITIONING OF CONNECTIONS TO IMPLEMENTS EVENT COUNTER
Event counter connector
OPERATION
AUTOTEST START-UP
PARTIAL EVENT COUNTER FUNCTION
TOTAL EVENT COUNTER FUNCTION
PARTIAL TRAVELLED DISTANCE FUNCTION
TOTAL TRAVELLED DISTANCE FUNCTION
PARTIAL WORKED SURFACE FUNCTION
TOTAL WORKED SURFACE FUNCTION
PARTIAL WORKED TIME FUNCTION
TOTAL WORKED TIME FUNCTION
INSTANTANEOUS SURFACE WORKED PER HOUR FUNCTION
Outside temperature function
TOOL WIDTH PROGRAMMING
INFOTRAC CALIBRATION PROCEDURE Operating speed
Procedure
1 – Set up 2 marks 100 metres apart on a level, straight and dry metalled road.
2 – Stop the tractor at approximately 15 to 20 meters before the first marker.
3 – With key (C), put index in front of symbol .
4 – Press key (C) for at least 3 seconds until the former calibration value and index under the Cal indication is displayed.
5 – Select a forward gear to enable an average speed of 7 km/ h to be attained.
6 – Use the clutch and accelerator manually to keep to a steady forward speed.
7 – When passing the first marker, press key (B), the former value disappears and a flashing value is displayed which changes proportionally to the travelled distance. This display indicates that calibration is in progress.
8 – As soon as the second marker is passed, press key (B) again.
9 – Briefly pressing key (C) validates the new calibration value.
10 – Pressing key (C) again returns the display to the partial event counter function.
CHAP-J-GB.pdf
J – WHEELS AND TYRES
REPLACEMENT OF TYRES, USE OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF TYRE
Special case of tractors with four wheel drive
Front/Rear inter-axle ratio
TYRE PRESSURES
Operating on soft ground (to improve grip)
Operating on hard ground (on the road, towing, etc.)
front and rear axle characteristics
Tyres and tracks
The front track is the distance at ground level between the centres of the front tyres. The rear track is the distance between the centres of the rear tyres at ground level.
Tyre combinations
Available in 4 WD
Available in 2 WD
Tables of front tracks 2 WD
Tables of front tracks 4 WD
Tables of front tracks 4 WD
Tables of front tracks 4 WD
Tables of front tracks 4 WD
Tables of rear tracks
Tables of rear tracks
SETTING THE TRACK
Front axle (2 wheel drive)
Front and rear axle
Tracking method
STEERING STOPS
Adjustment
CHAP-K-GB.pdf
K – Dimensions, weights, capacities and ballast
Dimensions
(with standard tyres)
Dimensions roll bar version
(with standard tyres)
*Value for version with downward exhaust
When they leave the production line, tractors are ballasted to behave normally in most operating situations. However, depending on working conditions, the ballast can be changed.
Capacities
The table below indicates the quantities of lubricant and fluid to be used in each component.
Only use recommended lubricants and fluids.
When topping up, the oil or fluid category must not be changed.
Regular oil changes are essential.
* See chapter G.
CHAP-L-GB.pdf
L – Maintenance
General cleaning
High-pressure cleaning systems
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
Touching up paintwork
FAILURES OR MALFUNCTIONS
Decrease in fluid level
Quantity and type of oil
Grease quality
Cab air filter: Cleaning
Windscreen washer fluid level: Check
Diesel fuel strainer: Cleaning
Wheel drive mechanical clutch clearance: Check
Engine oil level: Check
I – : Normal operating level.
II – : Top up as soon as possible.
III – : Top up before restarting the engine.
Elimination of dust accumulated inside the air filter: Cleaning
Elimination of water in the fuel: Cleaning
Coolant level: Check
Bleeding air from the pneumatic brake system: Check
Pneumatic braking connectors: Check – greasing
Pneumatic braking oil level: Check
Hydraulic fluid level: Check
(C) Maximum level.
(D) Minimum level.
(E) Correct level of use.
Front loader: Lubrication
Air conditioning compressor
Lubricating the compressor
Radiator grills: Cleaning
Front axle swing bearings : Lubrication
Rear lift: Lubrication
Front linkage: Lubrication
Front power take-off box oil level: Check
Tightness of the frontal loader adaptation: Check
Front axle final drive oil level: Check
Front axle differential unit oil level: Check
Front driven axle king pins: Lubrication
Wheel disc and rim nuts: Check
Tyre inflation pressure: Check
Front weight attachment bolts: Check
Cab recycled air filter: Check – change
Front power take-off box oil: Replace
Battery terminals: Cleaning – greasing
Front axle drive shaft main bearing: Lubrication
Engine oil: Replace
Engine oil filter cartridge: Replace
1 – Celtis 426, 436, 446
2 – Celtis 456
Diesel fuel filter cartridges: Replace
Line filter
3 – Celtis 426, 436, 446
4 – Celtis 456
Belts: Check – change
Replacement
Position of belt
G – Alternator.
H – Tensioner roller.
I – Water pump.
J – Crankshaft.
K – Air conditioning compressor.
L – Return roller.
M – Fan pulley.
N – Pneumatic brake compressor:
1 – Celtis 426 – 436 – 446.
2 – Celtis 456.
Front axle king pins: Lubrication
Front axle swing hinge pin: Lubrication
Front axle final drive oil: Replace
Hydraulic/transmission system filter cartridges: Replace
High pressure filter
Electro-hydraulic reverser filter
Bleeding air from the circuit
Mechanical power take-off clutch free travel: Check
Foot brake clearance: Check
Tightness of front and rear linkage hydraulic hoses
Front axle differential casing oil: Replace
Front axle breather: Replace
Hydraulic/transmission oil: Replace
Hydraulic/transmission oil: Replace (cont)
Hydraulic strainer: Replace
Rear axle breather: Replace
Hand brake clearance: Check
Engine air filter: Replace
Main cab air filter: Replace
Diesel fuel strainer: Replace
Hydraulic system accumulator: Check
Engine maintenance: Check – change
Air conditioning dehumidifier: Replace
MAINTENANCE RECORD
Operations to be carried out every 500 h
Operations to be carried out every 1000 h
Operations to be carried out every 2000 h
CHAP-M-GB.pdf
M – Operations that are mandatory under the guarantee
OPERATIONS MANDATORY UNDER THE TERMS OF THE CONTRACTUAL GUARANTEE
Pre-delivery inspection – Handing over to the customer
a) Pre-delivery inspection
Your CLAAS agent is responsible for preparing your tractor before delivery:
– Cleaning.
– General checks.
– Inspections.
He must stamp and sign it after checking and confirming the service handbook inspections.
If you wish, he can also install any certified equipment or after-sales options (air-conditioning, front power take-off and linkage, radio, etc.).
b) Handing over to the customer
Your supplier must provide you with the use and servicing handbook on delivery. He must explain this document and carry out a test, with you, in the field in order to familiarise you with your new tractor, and to answer all your questions.
The Acknowledgement of receipt, Pre-delivery inspection and Delivery to the customer sheets (to be found in the service handbook) must be filled in and signed by the technician responsible for the handover, and signed by the user.
On of the copies of the acknowledgement of receipt remains in the service handbook which is given to the user. The other copies are intended for CLAAS.
MANDATORY ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
HYDROSTATIC STEERING
FRONT DRIVE TRAIN – FRONT AXLE
TRANSMISSION – LINKAGE
WHEELS AND TYRES
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Battery:
Instrument panel:
Lighting:
Heating, ventilation, cooling:
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
HYDROSTATIC STEERING
FRONT DRIVE TRAIN – FRONT AXLE
TRANSMISSION – LINKAGE
WHEELS AND TYRES
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Battery:
Instrument panel:
Lighting:
Heating, ventilation, cooling.
TDM-FR_GBA.pdf
CONTENTS
IDENTIFICATION – CERTIFICATION – SAFETY
Tractor identification A.2
Certification A.3
Loader identification A.3
SAFETY A.4
Failure to comply with rules for safety and use A.4
Safety stickers with warning pictograms A.14
Controls and driving position B.2
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS (panel) B.3
Indicator and control lights B.4
ALARMS B.5
DIGITAL DISPLAYS B.7
DRIVER’S SEAT B.8
Controls and accessories in the cab roof B.9
Controls and accessories B.9
Recommendation B.14
Roll bar
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS (panel) B.16
DRIVER’S SEAT B.17
Electrical system (cab)
CHARACTERISTICS C.2
Electrical system (roll bar)
CHARACTERISTICS D.2
Operations before start D.3
STARTING THE ENGINE D.4
Engine starting help when cold D.5
STOPPING THE ENGINE D.5
OPERATION D.6
Bleeding air from the injection system D.9
Transmission
Revershift, Twinshift or hydraulic doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in the road range E.2
Mechanical doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in road range E.4
Without doubler with 4 or 5 gears (30 or 40 km/h) in road range E.6
Tables of forward speeds E.7
Clutch E.8
GEAR BOX E.9
Range selection E.12
Selection of the crawling speed E.12
Differential E.12
BRAKING E.13
PTO E.14
Procedure for setting off again E.15
Hitching-up and towing PTO attachments E.16
Stationary working E.17
Towing the tractor E.17
FRONT AXLE
CHARACTERISTICS F.2
Front axle engagement F.3
Hydraulics – rear linkage and hitch
CHARACTERISTICS G.2
Rear lift G.3
Auxiliary spool valves G.6
Linkage (Electronic Tracto-Control) TCE 9 G.11
Instructions for adjusting the rear hitch G.18
Automatic hitching G.21
FRONT POWER TAKEOFF, LINKAGE AND FRONT COUPLING – Front loader
Characteristics H.2
Front loader H.3
Frontal loader control H.7
Unhitching of the frontal loader H.8
Linkage of the frontal loader H.11
Linkage of the tool H.13
Unhitching of the tool H.14
Level indicator H.15
PCH system H.15
Maintenance on the tractor with frontal loader H.15
On board computer
On-board computer (INFOTRAC) I.2
OPERATION I.4
INFOTRAC CALIBRATION PROCEDURE Operating speed I.8
WHEELS AND TYRES
GENERAL J.2
TYRE PRESSURES J.2
front and rear axle characteristics J.4
Tyres and tracks J.5
SETTING THE TRACK J.13
STEERING STOPS J.15
Dimensions, weights, capacities and ballast
DIMENSIONS K.2
Dimensions roll bar version K.3
Weight K.4
Ballast K.4
Capacities K.5
MAINTENANCE
GENERAL L.2
Operations that are mandatory under the guarantee
OPERATIONS MANDATORY UNDER THE TERMS OF THE CONTRACTUAL GUARANTEE M.2
CHAP-A-GB.pdf
A – IDENTIFICATION – CERTIFICATION – SAFETY
Tractor identification
A – Tractor type.
B – Tractor identification number.
C – CEE number.
D – Maximum allowable gross weight depending on tyre fit (in kg).
E – Front axle weight.
F – Rear axle weight.
G – Maximum unbraked trailer weight (in kg).
H – Maximum trailer weight – mechanical brake (in kg).
I – Maximum trailer weight – inertia brake (in kg).
J – Maximum trailer weight – servo brake (in kg).
K – EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) acceptance.
L – EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) acceptance N°.
M – Smoke absorption coefficient.
N – CEE structure acceptance.
O – CEE structure acceptance N°.
Certification
CERTIFICATE OF COMPLIANCE
Loader identification
CERTIFICATE OF COMPLIANCE
FOREWORD
PRECAUTIONS BEFORE STARTING
Failure to comply with rules for safety and use
CONDITION OF THE TRACTOR
ADJUSTMENT OR MAINTENANCE – REPAIRS
AXLE STANDS
Hydraulic systems
Electrical system
Re-fuelling
ROAD USE – USE FOR TRANSPORT
Using the tractor
GENERAL RULE
WHEEL TRACK
ATTACHING IMPLEMENTS
STATIONARY WORK
USE OF TOOLS DRIVEN BY THE PTO
Using the loader
GENERAL RULE
Axle load
TOXIC PRODUCTS
IMPORTANT
Air conditioning
RECOMMENDATIONS:
IMPORTANT
SAFETY CABS
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
Safety stickers with warning pictograms
Cautions
Pictogram
Location
This tractor must not be operated at a speed greater than 30 km/h on public roads.
CHAP-B-GBA.pdf
Controls and driving position
Installation A – With Tracto Control hydraulic lift.
Installation B – With TCE 9 electrohydraulic lift.
1 – Hand brake lever.
2 – Passenger seat.
3 – Range lever.
4 – Gear lever/impulse contactor hydraulic doubler*.
5 – Cross control lever locking control.
6 – Auxiliary distributor cross control.
7 – Lift control lever (position control).
8 – Accelerator lever.
9 – Contactor plate (4 driving wheels, front power take- off…).
10 – Lift control lever (force control).
11 – Ashtray.
12 – Cigarette lighter.
13 – Hitch hook release lever.
14 – Power take-off clutch release lever (hydraulic engagement version ).
15 – Auxiliary distributor control lever.
16 – Power take-off rate selection lever.
17 – Crawler range selection lever.
18 – Power take-off clutch release lever (mechanical engagement version).
19 – TCE 9 Electronic tracto-control lift.
20 – Clutch pedal.
21 – Rear live axle differential claw pedal.
22 – Brake pedals.
23 – Accelerator pedal.
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS (panel)
1 – Hydroelectric forward/reverse lever (REVERSHIFT) .
2 – Air vents.
3 – Instrument cluster.
4 – Rotating light control button.
5 – Emergency alarm button.
6 – Mechanical range doubler lever.
7 – Main switch (key operated).
8 – Windscreen wipers.
9 – Windscreen washers.
10 – Direction indicators, lighting and warning lights.
11 – ventilation /air conditioning control panel.
12 – Steering wheel height/angle adjustment control.
13 – Digital clock adjustment knob (assembly B).
14 – Mechanical drive reverser lever.
Indicator and control lights
1 – Fuel low level warning light.
2 – Main beam indicator.
3 – 2nd trailer direction indicators repeater.
4 – 1st trailer direction indicators repeater.
5 – Tractor direction indicators repeater.
6 – Rear power take-off indicator.
7 – Front power take-off indicator.
8 – Not used.
9 – Hand brake warning light.
10 – Battery charge warning light.
11 – Emergency stop light.
12 – Engine oil pressure warning light.
13 – Hydraulic doubler oil pressure warning light.
14 – Transmission oil temperature warning light.
15 – Blocked dry type a
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
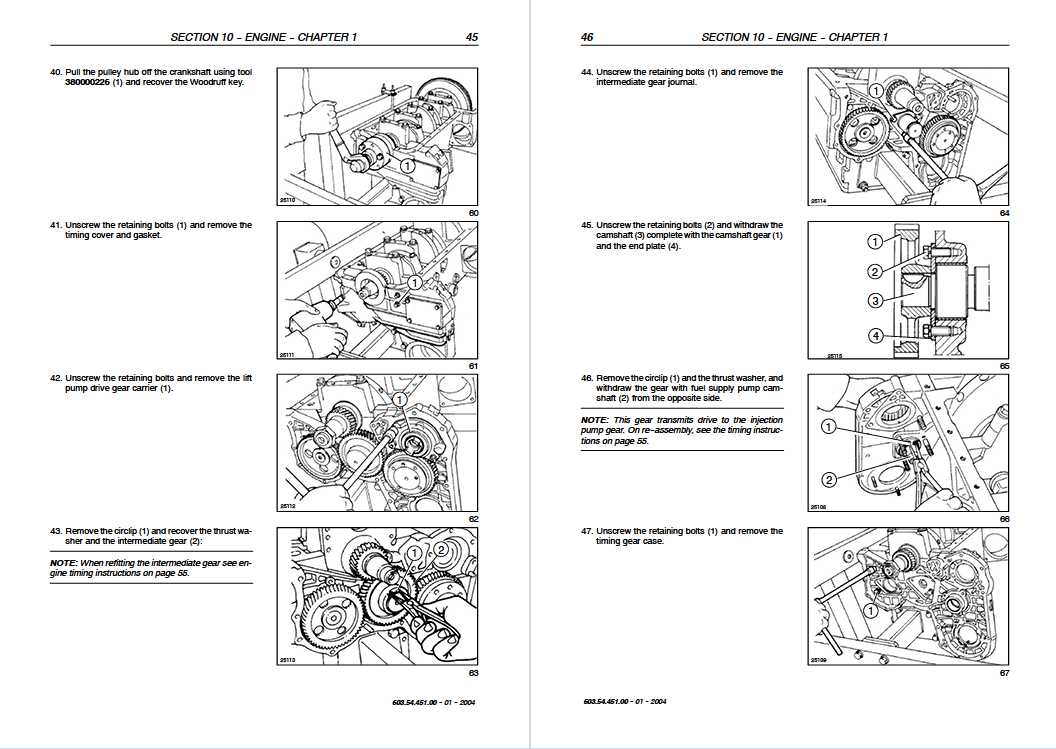
John Deere Transmission Control Unit Component Technical Manual CTM157 15JUL05
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
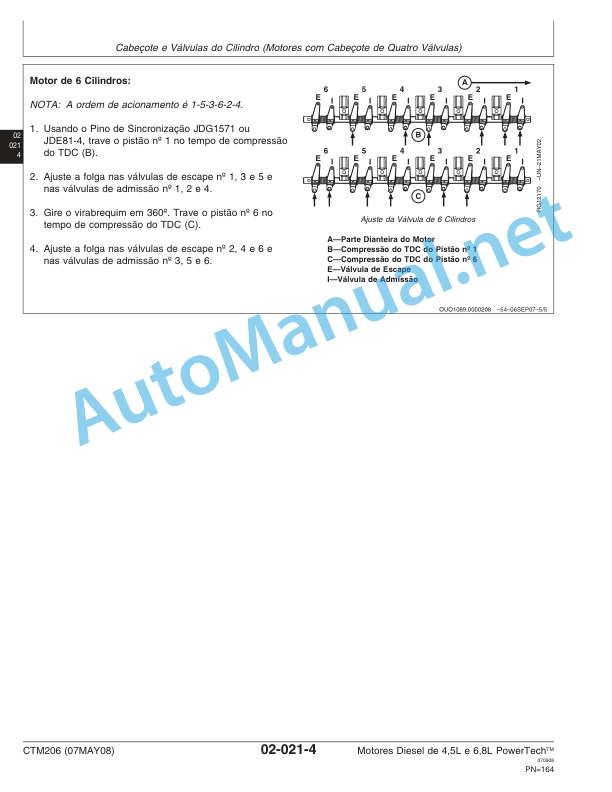
John Deere Diesel Engines PowerTech 4.5L and 6.8L – Motor Base Technical Manual 07MAY08 Portuguese
New Holland Service Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere DF Series 150 and 250 Transmissions (ANALOG) Component Technical Manual CTM147 05JUN98
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
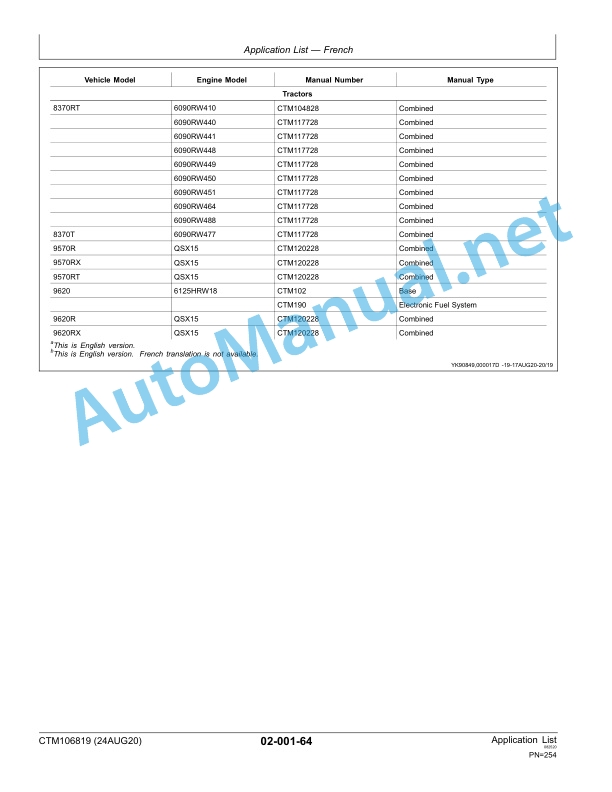
John Deere Application List Component Technical Manual CTM106819 24AUG20
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF