Claas Arion 640 630 620 610 600 (A19) Tractors Operator Manual ES
$50.00
- Model: Arion 640 630 620 610 600 (A19) Tractors
- Type Of Manual: Operator Manual
- Language: ES
- Format: PDF(s)
- Size: 88.6 MB
File List:
00 1116 973 0.pdf
00 1121 950 4.pdf
00 1121 977 4.pdf
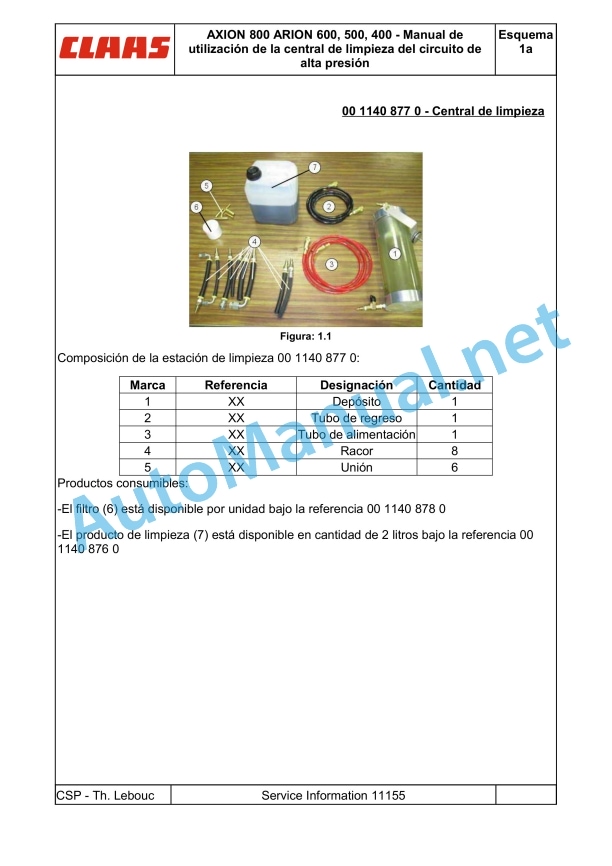
00 1140 877 0.pdf
00 1170 297 2.pdf
00 1171 316 0.pdf
00 2182 368 0.pdf
00 1116 973 0.pdf:
recommendations
For your security
Use according to the purpose
Description
Description: Chapter symbols
A – Identification – Homologation – Safety
tractor plate
Drive plate
Homologation
Security
Security instructions
Safety stickers with warning pictograms
B – Driving position
Driving and working environment
Controls and instruments (cockpit)
Controls and instruments (dashboard)
Accommodations and accessories
Lighting, signaling and security
Description
Driving lights and acoustic warning
Work lights and rotating headlight
Roof light
General key contactor
Description
Multifunction armrest
Adjustment
Utilization
steering wheel
Adjustment
Dashboard
Description
Functioning
Utilization
Calibration
Visualizer
Transmission display (digital)
Natural aeration and crystals
Utilization
Heating – ventilation – manual air conditioning
Description
Utilization
Heating/ventilation automatic air conditioning
Description
Utilization
cab suspension
Adjustment
C – Electricity
Trailer/tool lighting socket
Description
Power socket electrical box
Description
Taking the event counter
Description
Take ISO
Description
Predisposition to install a control box in the cabin
Fixing the box support
Cable routing
Description
battery switch
Description
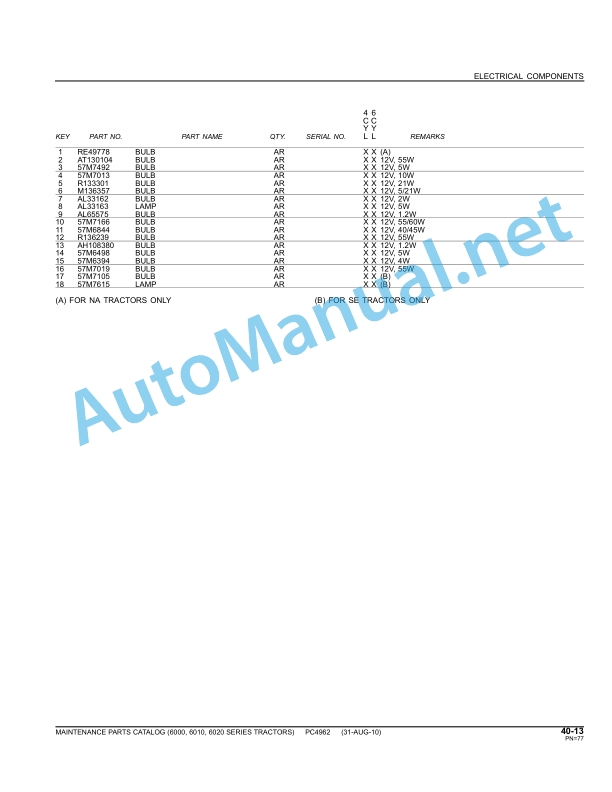
Fuses and relays
recommendations
Cab service fuse box
Upper cabin fuse box
Primary Service Fuse Box
D -Motor
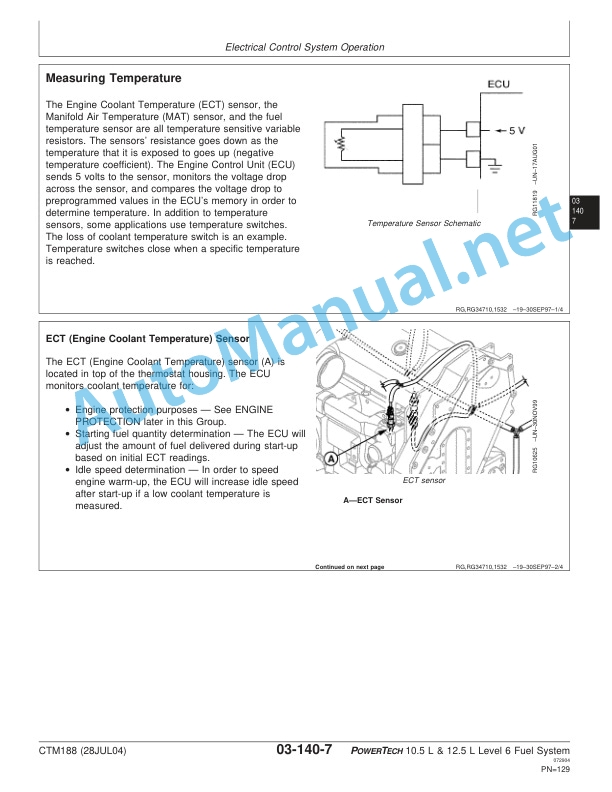
Characteristics
Characteristics
Visualizers
Description
Security
Safety: Mechanical protection
engine control
Engine start
throttle controls
Engine stop
Claas power management
Functioning
recommeions
Eransmission
Transmission characteristics
Feed speed
rear axle
power take-offs
Visualizers
Transmission display (digital)
Dashboard
Security
Neutral inverter
Neutral transmission
Mechanical protection
Set in motion
Manual gear operation
Automatic gear change
Relationship management
Reduced range
rear axle
Locking differentials
Tractor braking
Trailer braking
power take off
Permanent job
Obligations
Obligations
F – Front axle
Front bridge
Characteristics
Mechanical protection
Functioning
Dashboard
Front axle gear
Functioning
Automatic mode
Permanent mode
Proactiv Suspension
Functioning
Fixed mode
Automatic mode
G – Hydraulic system – rear lift and hitch
Characteristics
Hydraulic
Elevation
Hydraulic
Auxiliary distributors
Power beyonD
Elevation
Controls
Security
Lift start-up
Mode selection
Position control
Effort control
High stop
Descent speed
Transport shock absorber
Active skating management
External controls
recommendations
Fixing mechanisms
Upper connecting rod
Stabilizers
Automatic hooks
hitch bolts
Bar with ball
Pickup hitch
H – Front power take-off – lifting and front hitch
Front loader
Characteristics
Electropilot
flexpilot
Charger release
Charger hitch
Tool attachment
Tool release
Level indicator
PCH system
Intervention on the tractor with loader
I -On-board computer
Claas Information System
Description
Utilization
J – Wheels and tires
recommendations
inflation pressure
Wheel pairing
Features: commissioning
front tracks
rear tracks
Tire combinations
Particular cases
Tools that work at great depth
K – Dimensions, weights, capacities and ballast
Dimensions and weights
Description
Capabilities
Description
Ballasted
Description
L – Maintenance
Generalities
recommendations
Periodicity
Summary table
Operations
Bleeding air from the injection circuit
Description
Logbook of maintenance operations
recommendations
M – Mandatory guarantee operations
Mandatory operations carried out within the framework of the contractual guarantee
Inspection before delivery – Delivery to customer
Maintenance operations to be carried out
Mandatory visits
00 1121 950 4.pdf:
. Information about this user manual
. Validity of the instructions for use
. Chapter symbols
A – Identification – Homologation – Safety
1. Tractor signal plate
2. Tractor power label
3. Engine signal plate
4. Cabin nameplate
5. European regulations
6. Security
6.1. Security instructions
6.1.1. Use according to the purpose
6.1.2. Use not in accordance with assignment
6.1.3. Precautions to be taken before starting up
6.1.4. Tractor status
6.1.5. Adjustment or maintenance work – repairs
6.1.5.1. General rule
6.1.5.2. Placement on lifting arms
6.1.5.3. Electricity
6.1.5.4. Fuel
6.1.5.5. Coolant liquid
6.1.6. Circulation – Transport
6.1.7. Tractor use
6.1.7.1. General rule
6.1.7.2. Tractor wheelbase
6.1.7.3. Tool attachment
6.1.7.4. Driving
6.1.7.5. Permanent jobs
6.1.7.6. Work with tools powered by the power take-off
6.1.7.7. Severe applications
6.1.8. Toxic products
6.1.9. Air-conditioning
6.1.10. Cabin
6.1.11. passenger seat
6.1.12. Respect for the environment
6.1.13. Using a front loader
6.1.14. Forestry applications
6.2. Safety stickers with warning pictograms
6.2.1. recommendations
6.2.2. Putting the gearbox in neutral
6.2.3. Front lift
6.2.4. Front tow hook
6.2.5. User manual
6.2.6. passenger seat
6.2.7. Speed limit and child under 13 years old 6.2.8. Aonditioning
6.2.9. PTO 1,000 1/min
6.2.10. hydraulic hoses
6.2.11. External controls
6.2.12. start
6.2.13. Battery
6.2.14. Radar
6.2.15. PTO protection
6.2.16. High pressure cleaner
6.2.17. Accumulators
6.2.18. FOPS Roof
6.2.19. Wheel nuts
6.2.20. Electrohydraulic distributors
B – Cabin
1. Driving and working environment
1.1. Controls and instruments (cockpit)
1.2. Controls and instruments (dashboard)
1.3. Accommodations and accessories
2. Lighting, signage and security
2.1. Description
2.2. Low beam/high beam and klaxon
23. Work lights and rotating headlight
2.4. Roof light
2.5. Mirrors
2.6. Signal triangle
3. Start contactor
4. Multifunction elbow support
5. Seats
5.1. Driver’s seat
5.2. passenger seat
6. steering wheel
7. Dashboard
7.1. Description
7.2. Functioning
7.3. Utilization
7.4. Calibration
8. Visualizer
8.1. Cebis Terminal
9. Openers and glass
10. Viewer
11. Heating – ventilation – manual air conditioning
11.1. Description
11.2. Utilization
12. Heating/ventilation automatic air conditioning
12.1. Description
12.2. Utilization
13. Cabin suspension
C – ELECTRICITY
1. Features
2. Trailer/tool lighting socket
3. Power socket electrical box
4. Taking the event counter
5. ISO shooting
6. ISOBUS connection
7. Predisposition for the installation of a control box in the cabin
7.1. Fixing the box support
7.2. Cable routing
8. Battery
8.1. battery tray
8.2. battery switch
9. Fuses and relays
9.1. recommendations
9.2. Cab service fuse box
9.3. Upper cabin fuse box
9.4. Primary Service Fuse Box
D – Engine
1. Features
2. Visualizers
2.1. Dashboard
2.2. Cebis Terminal
3. Security
3.1. Functioning
3.2. Cebis Terminal
3.3. Dashboard
3.4. recommendations
4. Engine hood
4.1. Monobloc hood
4.2. Side hoods
5. Engine control
5.1. Engstart
5.1Preliminary operations
5.1.2. Start up
5.1.3. Helps start the engine in cold weather
5.2. Using the accelerator pedal and lever
5.2.1. Functioning
5.2.2. Accelerator pedal
5.2.3. manual throttle
5.2.4. Engine speed memories
5.2.4.1. Utilization
5.2.4.2. Adjustment procedure by Cebis
5.2.4.3. Manual adjustment procedure
5.3. Engine stop
6. CLAAS Power Management
7.1. recommendations
7.2. Bleeding air from the injection circuit
E – Transmission
1. Features
2. Forward speeds
3. Indication
3.1. Cebis Terminal
3.2. Dashboard
4. Security
4.1. Neutral inverter
4.1.1. Utilization
4.1.2. Functioning
4.2. Neutral transmission
4.2.1. Utilization
4.2.2. Functioning
4.3. Protection of mechanical organs
4.3.1. Functioning
4.3.2. Dashboard
4.3.3. Cebis Terminal
5. Setting in motion
5.1. Clutch
5.1.1. recommendations
5.1.2. Clutch pedal
5.1.3. reverse lever
5.2. Selection of feed direction
5.3. Inverter progressivity adjustment
5.3.1. Utilization
5.3.2. Adjustment
5.4. Engaging/disengaging front/rear speeds
5.4.1. Utilization
5.4.2. Adjustment
5.4.3. Functioning
6. Manual gear operation
6.1. Starting ratio
6.1.1. Functioning
6.1.2. Adjustment
6.2. Work mode
6.3. Transport mode
7. Automatic gear change
7.1. Skip shift
7.1.1. Utilization
7.1.2. Functioning
7.2. Automatic speed adaptation (Speed Matching)
7.2.1. Utilization
7.2.2. Functioning
7.3. Maneuvering ratio
7.3.1. Utilization
7.3.2. Adjustment
7.3.3. Functioning
7.4. Hexactiv
7.4.1. Utilization
7.4.2. Functioning
7.4.3. Selection of the automation regime
7.4.4. Demarcation of automation
7.4.4.1. Utilizn
7.4.4.2nctioning
7.4.5. Starting ratio in Hexactiv and transport mode
7.4.5.1. Utilization
7.4.5.2. Functioning
7.4.5.3. Adjustment
8. Super-slow range
8.1. Utilization
8.2. Functioning
9. Relationship Management
9.1. Functioning
rear axle
1. Features
2. Protection of mechanical organs
2.1. Functioning
2.2. Dashboard
23. Cebis Terminal
3. Locking differentials
3.1. recommendations
3.2. Functioning
3.3. Automatic mode
3.3.1. Utilization
3.3.2. Functioning
3.4. Permanent mode
3.4.1. Utilization
3.4.2. Functioning
4. Brakes
4.1. Service brakes
4.2. Parking brake
4.2.1. Obligations
4.2.2. Hand brake
5. Trailer braking
5.1. Hydraulic brake
5.2. pneumatic brake
F – Front axle
1. Features
2. Protection of mechanical organs
2.1. Functioning
2.2. Dashboard
23. Cebis Terminal
3. Front axle gear
3.1. Functioning
3.2. Automatic mode
3.2.1. Utilization
3.2.2. Functioning
3.3. Permanent mode
3.3.1. Utilization
3.3.2. Functioning
4. Suspended front axle
4.1. Functioning
4.2. Fixed mode
4.2.1. Utilization
4.2.2. Functioning
4.3. Automatic mode
4.3.1. Utilization
4.3.2. Functioning
G – Rear equipment
Hydraulic
1. Features
2. Auxiliary distributors
2.1. Association of rear controls/pressure taps
2.2. pressure taps
2.2.1. recommendations
2.2.2. Utilization
2.2.3. Free return to the warehouse
2.2.4. Oil recovery button
23. Controls
2.4. Security
2.4.1. Protection of mechanical organs
2.4.2. Cebis Terminal
2.5. Start up
2.5.1. Utilization
2.5.2. Display on the Cebis terminal
2.5.3. Functioning
2.6. Online controls
2.7. Cross control
2.8. External controls
2.9. Management of electrohydraulic distributors
2.9.1. Utilization
2.9.2. Visualizer
2.9.3. Maximum flow rate of a pressure tap
2.9.4. Hydraulic timer
2.9.5. Activation of the distributor on the exterior controls
2.9.6. Locking the electrohydraulic distributors
3. Power beyond
3.1. Description
3.2. Utilization
3.3. Functioning
4. Permanent job
rear lift
1. Features
2. Controls
3. Visualizer
4. Security
4.1. Protection of mechanical organs
4.2. safety pilot
4.3. Cebis Terminal
4.4. Transportation security
5. Lift start-up
6. Mode selection
7. Position control
8. Effort control
9. High cap
10. Download speed
11. Transport shock absorber
12. Active skating management
12.1. Utilization
12.2. Adjustment
12.3. Functioning
13. External controls
13.1. Utilization
13.2. Functioning
rear power take off
1. Features
2. Recommendations
3. Controls
4. Indication
5. PTO speed selection
6. Usage
7. External controls
8. Operation
9. PTO automation
9.1. Utilization
9.2. manual adjustment
9.3. Adjustment by Cebis terminal
10. PTO ferrule
11. Tool attachment on the power take-off
12. Permanent job
rear hitch
1. Features
2. Recommendations
3. Fixing mechanisms
4. Upper connecting rod
4.1. Mechanical upper connecting rod
4.2. Hydraulic upper connecting rod
5. Automatic hooks
6. Stabilizers
6.1. Utilization
6.2. Mechanical stabilizers
6.3. Self-Locking Stabilizers
7. Hitch Bolts
8. Swing bar
9. Bar with ball
10. Pickup hitch
H – Front equipment
Hydraulic
1. Features
2. Pressure taps
2.1. recommendations
2.2. UTILIZATION
23. Free return to the warehouse
2.4. Oil recovery button
3. Security
3.1. Protection of mechanical organs
3.2. Cebis Terminal
4. Description
5. Distributor controlled front pressure intakes 3
5.1. Controls
5.2. Preliminary operations
5.3. UTILIZATION
6. Distributor controlled front pressure intakes 7
6.1. Controls
6.2. Preliminary operations
6.3. UTILIZATION
7. Management of electrohydraulic distributors
Front lift
1. Features
2. Distributor Controlled Front Lift 1
2.1. Controls
2.2. Security
2.2.1. Private lockers
2.2.2. Protection of mechanical organs
2.2.3. Cebis Terminal
2.2.4. Transportation security
23. Preliminary operations
2.4. UTILIZATION
2.5. External controls
3. Distributor Controlled Front Lift 6
3.1. Controls
3.2. Security
3.2.1. Private lockers
3.2.2. Protection of mechanical organs
3.2.3. Cebis Terminal
3.3. Preliminary operations
3.4. UTILIZATION
3.5. External controls
4. 3-point hitch
4.1. lower cranks
4.2. Upper connecting rod
4.3. Hitching and unhitching the implement
front power take off
1. Features
2. Indication
3. Recommendations
4. Front PTO interlock
5. Front PTO stop
6. Adjustment
Front loader
1. Assembly of an adaptation structure for a front loader
I – Cebis Terminal
Using the Cebis terminal
1. Description
2. Operation
4. Multifunction display
4.1. Utilization
4.2. Work screen
4.3. Road screen
5. Direct Access
5.1. Utilization
5.2. Functioning
6. Operating anomalies
6.1. Functioning
6.2. Alarms
6.2.1. Description
6.2.2. Utilization
6.2.3. Functioning
6.3. Warning
6.3.1. Description
6.3.2. Utilization
6.3.3. Functioning
6.4. Information
6.4.1. Description
6.4.2. Utilization
6.4.3. Functioning
6.5. Icon
6.5.1. Description
6.5.2. Utilization
6.5.3. Functioning
7.1. Main menu
7.2. Transmission
7.3. Elevation
7.4. Hydraulic
7.5. On-board computer
7.6. CLAAS Sequence Management
7.7. Previewing a CLAAS Sequence Management sequence in real time
On-board computer
1. Usage
2. General features
2.1. Utilization
2.2. Programmable window parameterization
23. Resetting the counters to zero
3. Plot management
3.1. Utilization
3.2. Start/stop of counters
3.2.1. Procedure through Cebis
3.2.2. Manual procedure
3.3. Plot Management Editor
3.3.1. Utilization
3.3.2. Selecting a plot
3.3.3. Resetting the counters of a plot
4. Tool parameterization
4.1. Working width
4.2. counting mode
4.3. Selection of theoretical or real speed
4.4. Tool management
4.4.1. Utilization
4.4.2. Safeguarding the parameters of the tool in use
4.4.3. Registering a new tool
4.4.4. Loading a tool
4.4.5. Loading a CLAAS tool
4.4.6. Changing the name of a tool
4.4.7. Deleting a tool
5. Maintenance
5.1. Maintenance counter
5.1.1. Utilization
5.1.2. Resetting the counters to zero
5.2. List of active anomalies
5.3. Transmission oil temperature
6. Function contactors F1, F2, F3 and F4
6.1. Utilization
6.2. Adjustment
6.2.1. Description
6.2.2. Count
6.2.3. CLAAS Sequence Management
6.2.4. ISOBUS
6.2.5. Front loader
7. Cebis
7.1. Brightness
7.1.1. Automatic brightness adjustment
7.1.2. Manual brightness adjustment
7.2. Languages and units
7.2.1. Language
7.2.2. Units
7.3. Date and Time
CLAAS Sequence Management
1. Usage
2. Operation
3. Controls
3.1. Description
4. Security
4.1. Protection of mechanical organs
5. Launching a sequence
5.1. Utilization
5.2. Functioning
6. Recording a sequence
7. Interrupting a sequence
7.1. Momentary interruption of a sequence in progress
7.2finitive interruption omomentarily interrupted sequence
7.3. Permanent interruption of a sequence in progress
7.4. Interruption of ongoing actions
7.5. Emergency stop
8. Viewing a sequence
8.1. Display in info mode
8.1.1. Utilization
8.1.2. Description
8.2. Viewing in real time mode
8.2.1. Utilization
8.2.2. Description
9. Modifying a sequence
9.1. Utilization
9.2. Modifying a step in a sequence
9.3. Add a stage in a sequence
9.4. Deleting a step in a sequence
9.5. Selecting the recording mode of a sequence
J – Wheels and tires
1. Tires
1.1. recommendations
1.2. inflation pressure
1.2.1. Characteristics
1.2.2. recommendations
1.3. Load index
1.4. speed code
2. Paths
2.1. Commissioning
2.2. front tracks
2.2.1. Front bridge
2.2.2. Front Track Tables
2.2.3. Front axle swing stops
23. rear tracks
2.3.1. rear axle
2.3.2. Rear track boards
2.3.3. Track with smooth tree rear bridge
2.4. Tire combinations
3. WHEELS
K – Features
1. Dimensions
2. Weight
3. Loading capacities
4. Maximum permissible towable masses
5. Capacities
6. Weighted
6.1. Ballasts available
6.2. Tractor balancing
7. Cabin comfort
7.1. Sound level
7.2. vibration level
L – Maintenance
1. Recommendations
2. Trailer
3. Transportation
4. Using a jack
5. Changing a wheel
6. Tractor loading and stowage
7. Parking
8. Disablement and destruction
9. Periodicities
9.1. Summary table
9.2. Operations
9.2.1. Operation #1
9.2.2. Operation #2
9.2.3. Operation #3
9.2.4. Operation #4
9.2.5. Operation #5
9.2.6. Operation #6
9.2.7. Operation #7
9.2.8. Operation #8
9.2.9. Operation #9
9.2.10. Operation #10
9.2.11. Operation #11
9.2.12. Operation #12
9.2.13. Operation #13
9.2.14. Operation #14
9.2.15. Operation #15
9.2.16. Operation #16
9.2.17. Operation #17
9.2.18. Operation #18
9.2.19. Operation #19
9.2.20. Operation #20
9.2.21. Operation #21
9.2.22. Operation #22
9.2.23. Operation #23
9.2.24. Operation #24
9.2.25. Operation #25
9.2.26. Operation #26
9.2.27. Operation #27
9.2.28. Operation #28
9.2.29. Operation #29
9.2.30. Operation #30
9.2.31. Operation #31
9.2.32. Operation #32
9.2.33. Operation #33
9.2.34. Operation #34
9.2.35. Operation #35
9.2.36. Operation #36
9.2.37. Operation #37
9.2.38. Operation #38
9.2.39. Operation #39
9.2.40. Operation #40
9.2.41. Operation #41
9.2.42. Operation #42
9.2.43. Operation #43
9.2.44. Operation #44
9.2.45. Operation #45
9.2.46. Operation #46
9.2.47. Operation #47
9.2.48. Operation #48
9.2.49. Operation #49
9.2.50. Operation #50
9.2.51. Operation #51
9.2.52. Operation #52
9.2.53. Operation #53
9.2.54. Operation #54
9.2.55. Operation #55
9.2.56. Operation #56
9.2.57. Operation #57
9.2.58. Operation #58
9.2.59. Operation #59
9.2.60. Operation No. 60
9.2.61. Operation #61
9.2.62. Operation No. 62
9.2.63. Operation No. 63
10. Bleeding the air from the injection circuit
11. Maintenance operations logbook
M – Mandatory warranty operations
1. MANDATORY OPERATIONS CARRIED OUT WITHIN THE FRAMEWORK OF THE CONTRACTUAL WARRANTY
1.1. Inspection before delivery
1.2. Customer delivery
1.3. MAINTENANCE OPERATIONS TO BE CARRIED OUT
1.4. Mandatory visits
1.4.1. Mandatory inspection after the first 100 hours
1.4.2. Mandatory inspection after the first 500 hours
Alphabetical index
00 1121 977 4.pdf:
. Information about this user manual
. Validity of the instructions for use
. Chapter symbols
A – Identification – Homologation – Safety
1. Tractor signal plate
2. Tractor power label
3. Engine signal plate
4. Cabin nameplate
5. European regulations
6. Security
6.1. Security instructions
6.1.1. Use according to the purpose
6.1.2. Use not in accordance with assignment
6.1.3. Precautions to be taken before starting up
6.1.4. Tractor status
6.1.5. Adjustment or maintenance work – repairs
6.1.5.1. General rule
6.1.5.2. Placement on lifting arms
6.1.5.3. Electricity
6.1.5.4. Fuel
6.1.5.5. Coolant liquid
6.1.6. Circulation – Transport
6.1.7. Tractor use
6.1.7.1. General rule
6.1.7.2. Tractor wheelbase
6.1.7.3. Tool attachment
6.1.7.4. Driving
6.1.7.5. Permanent jobs
6.1.7.6. Work with tools powered by the power take-off
6.1.7.7. Severe applications
6.1.8. Toxic products
6.1.9. Air-conditioning
6.1.10. Cabin
6.1.11. passenger seat
6.1.12. Respect for the environment
6.1.13. Using a front loader
6.1.14. Forestry applications
6.2. Safety stickers with warning pictograms
6.2.1. recommendations
6.2.2. Putting the gearbox in neutral
6.2.3. Front lift
6.2.4. Front tow hook
6.2.5. User manual
6.2.6. passenger seat
6.2.7. Speed limit and child under 13 years old
6.2.8. Air conditioning
6.2.9. PTO 1,000 1/min
6.2.10. hydraulic hoses
6.2.11. External controls
6.2.12. start
6.2.13. Battery
6.2.14. Radar
6.2.15. PTO protection
6.2.16. High pressure cleaner
6.2.17. Accumulators
6.2.18. FOPS Roof
6.2.19. Wheel nuts
6.2.20. Electrohydraulic distributors
B – Cabin
1. Driving and working environment
1.1. Controls and instruments (cockpit)
1.2. Controls and instruments (dashboard)
1.3. Accommodations and accessories
2. Lighting, signage and security
2.1. Description
2.2. Low beam/hieam and klaxon
23. Work lights and rotating headlight
2.4. Roof light
2.5. Mirrors
2.6. Signal triangle
3. Start contactor
4. Multifunction elbow support
5. Seats
5.1. Driver’s seat
5.2. passenger seat
6. steering wheel
7. Dashboard
7.1. Description
7.2. Functioning
7.3. Utilization
7.4. Calibration
8. Visualizer
8.1. Transmission display
9. Openers and glass
10. Viewer
11. Heating – ventilation – manual air conditioning
11.1. Description
11.2. Utilization
12. Heating/ventilation automatic air conditioning
12.1. Description
12.2. Utilization
13. Cabin suspension
C – ELECTRICITY
1. Features
2. Trailer/tool lighting socket
3. Power socket electrical box
4. Taking the event counter
5. ISO shooting
6. ISOBUS connection
7. Predisposition for the installation of a control box in the cabin
7.1. Fixing the box support
7.2. Cable routing
8. Battery
8.1. battery tray
8.2. battery switch
9. Fuses andays
9.1. recommendations
9.2. Cab service fuse box
9.3. Upper cabin fuse box
9.4. Pry Service Fuse Box
D – Engine
1. Features
2. Visualizers
2.1. Dashboard
3. Security
3.1. Functioning
3.2. Dashboard
3.3. recommendations
4. Engine hood
4.1. Monobloc hood
4.2. Side hoods
5. Engine control
5.1. Engine start
5.1.1. Preliminary operations
5.1.2. Start up
5.1.3. Helps start the engine in cold weather
5.2. Using the accelerator pedal and lever
5.2.1. Functioning
5.2.2. Accelerator pedal
5.2.3. manual throttle
5.2.4. Engine speed memories
5.2.4.1. Utilization
5.2.4.2. Manual adjustment procedure
5.3. Engine stop
6. CLAAS Power Management
7.1. recommendations
7.2. Bleeding air from the injection circuit
E – Transmission
1. Features
2. Forward speeds
3. Indication
3.1. Transmission display
3.2. Dashboard
4. Security
4.1. Neutral inverter
4.1.1. Utilization
4.1.2. Functioning
4.2. Neutral transmission
4.2.1. Utilization
4.2.2. Functioning
4.3. Protection of mechanical organs
4.3.1. Functioning
4.3.2. Dashboard
4.3.3. Transmission display
5. Setting in motion
5.1. Transmission display
5.2. Clutch
5.2.1. recommendations
5.2.2. Clutch pedal
5.2.3. reverse lever
5.3. Selection of feed direction
5.4. Inverter progressivity adjustment
5.4.1. Utilization
5.4.2. Adjustment
5.5. Engaging/disengaging front/rear speeds
5.5.1. Utilization
5.5.2. Adjustment
5.5.3. Functioning
6. Manual gear operation
6.1. Starting ratio
6.1.1. Functioning
6.1.2. Adjustment
6.2. Work mode
6.3. Transport mode
7. Automatic gear change
7.1. Skip shift
7.1.1. Utilization
7.1.2. Functioning
7.2. Automatic speed adaptation (Speed Matchin 7.2.1. Utilization
7.2.2. Functioning
7.3. Maneuvering ratio
7.3.1. Utilizn
7.3.2. Adjustment
7.3.3. Functioning
7.4. Hexactiv
7.4.1. Utilization
7.4.2. Functioning
7.4.3. Selection of the automation regime
7.4.4. Demarcation of automation
7.4.4.1. Utilization
7.4.4.2. Functioning
7.4.5. Starting ratio in Hexactiv and transport mode
7.4.5.1. Utilization
7.4.5.2. Functioning
7.4.5.3. Adjustment
8. Relationship Management
8.1. Functioning
8.2. Transmission display
9. Super-slow range
9.1. Utilization
9.2. Functioning
rear axle
1. Features
2. Locking differentials
2.1. recommendations
2.2. Functioning
23. Automatic mode
2.3.1. Utilization
2.3.2. Functioning
2.4. Permanent mode
2.4.1. Utilization
2.4.2. Functioning
3. Protection of mechanical organs
3.1. Functioning
3.2. Dashboard
3.3. Transmission display
4. Brakes
4.1. Service brakes
4.2. Parking brake
4.2.1. Obligations
4.2.2. Hand brake
4.3. High pressure braking
5. Trailer braking
5.1. Hydraulic brake
5.2. pneumatic brake
F – Front axle
1. Features
2. Protection of mechanical organs
2.1. Functioning
2.2. Dashboard
3. Front axle gear
3.1. Functioning
3.2. Automatic mode
3.2.1. Utilization
3.2.2. Functioning
3.3. Permanent mode
3.3.1. Utilization
3.3.2. Functioning
4. Suspended front axle
4.1. Functioning
4.2. Fixed mode
4.2.1. Utilization
4.2.2. Functioning
4.3. Automatic mode
4.3.1. Utilization
4.3.2. Functioning
G – Rear equipment
Hydraulic
1. Features
2. Open center circuit
2.1. Association of rear controls/pressure taps
2.2. pressure taps
2.2.1. recommendations
2.2.2. Utilization
2.2.3. Free return to the warehouse
2.2.4. Oil recovery button
23. Controls
2.4. Control levers
2.5. Flow divider
2.6. Double acting/single acting conversion
3. Center with closed center
3.1. Association of rear controls/pressure taps
3.2. pressure taps
3.2.1. recommendations
3.2.2. Utilization
3.2.3. Free return to the warehouse
3.2.4. Oil recovery button
3.3. Controls
3.4. Control levers
3.5. Adjustment of the flow of the distributors with mechanical control
3.6. Power beyond
3.6.1. Description
3.6.2. Utilization
3.6.3. Functioning
4. Permanent job
rear lift
1. Features
2. Controls
3. Security
3.1. Protection of mechanical organs
3.2. safety pilot
3.3. Transportation security
4. Lift start-up
5. Mode selection
6. Position control
7. Effort control
8. High cap
9. Download speed
10. Transport shock absorber
11. Active skating management
11.1. Utilization
11.2. Adjustment
11.3. Functioning
12. External controls
12.1. Utilization
12.2. Functioning
rear power take off
1. Features
2. Recommendations
3. Controls
4. Indication
5. PTO speed selection
6. Usage
7. External controls
8. Operation
9. PTO automation
9.1. Utilization
9.2. Adjustment
10. PTO ferrule
11. Tool attachment on the power take-off
12. Permanent job
rear hitch
1. Features
2. Recommendations
3. Fixing mechanisms
4. Upper connecting rod
4.1. Mechanical upper connecting rod
4.2. Hydraulic upper connecting rod
5. Automatic hooks
6. Stabilizers
6.1. Utilization
6.2. Mechanical stabilizers
6.3. Self-Locking Stabilizers
7. Hitch Bolts
8. Swing bar
9. Bar with ball
10. Pickup hitch
H – Front equipment
Hydraulic
1. Features
2. Front pressure intakes controlled by distributor 3
2.1. Association of front pressure controls/intakes
2.2. pressure taps
2.2.1. recommendations
2.2.2. UTILIZATION
2.2.3. Free return to the warehouse
2.2.4. Oil recovery button
23. UTILIZATION
2.4. Flow adjustment
3. Distributor controlled front pressure intakes 7
3.1. Association of front pressure controls/intakes
3.2. pressure taps
3.2.1. recommendations
3.2.2. UTILIZATION
3.2.3. Free return to the warehouse
3.2.4. Oil recovery button
3.3. Security
3.3.1. Protection of mechanical organs
3.3.2. C.I.S Terminal
3.4. Preliminary operations
3.5. UTILIZATION
3.6. Management of electrohydraulic distributors
3.6.1. Description
3.6.2. White pressure tap flow adjustment
3.6.3. Black pressure port flow adjustment
3.6.4. Hydraulic timer
Front lift
1. Features
2. Distributor Controlled Front Lift 1
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere DF Series 150 and 250 Transmissions (ANALOG) Component Technical Manual CTM147 05JUN98
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere POWERTECH E 4.5 and 6.8 L Diesel Engines TECHNICAL MANUAL 25JAN08
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere 18-Speed PST Repair Manual Component Technical Manual CTM168 10DEC07
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF