- Claas
- Grove
- New Holland
- Komatsu
- Kubota
- John Deere
- Linde
- Bomag
- CASE
- Clark
- JCB
- Jungheinrich
- Linde
- Yale
- Yanmar
- Manitou
- Manitowoc
- CNH
- Doosan
- Fiatagri
- Fiatallis
- Fiatallis Other Manual PDF
- Flexi Coil
- Ford New Holland
- Ford New Holland Other Manual PDF
- Huyndai
- Hypac
- Hyster
- Hyster Service Manual PDF
- Isuzu
- Kobelco
- Kohler
- Krupp
- Lombardini
- Mahindra
- Nuvera
- Perkins
- Sperry New Holland
- Utilev
- Versatile
- ZF
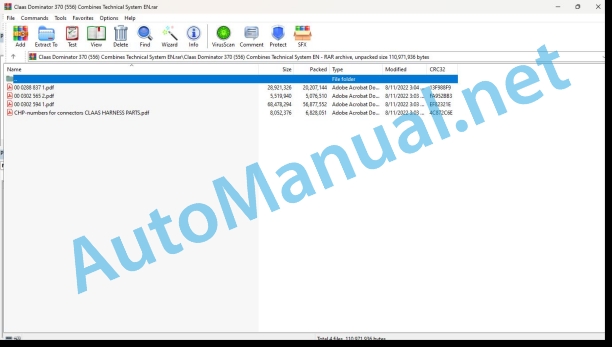
Claas Dominator 370 (556) Combines Technical System EN
$300.00
- Model: Dominator 370 (556) Combines
- Type Of Manual: Technical System
- Language: EN
- Format: PDF(s)
- Size: 84.9 MB
File List:
00 0288 837 1.pdf
00 0302 565 2.pdf
00 0302 594 1.pdf
CHP-numbers for connectors CLAAS HARNESS PARTS.pdf
00 0288 837 1.pdf:
PERKINS 1106D – E70TA
Table of contents
CCN explanation
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
Electric systems standard
Overview
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
Introduction
Validity of manual
Validity of manual
Safety rules
Safety and hazard information
General information
Important!
Hazard signs
Signal word
Regulations for avoiding accidents with personal injuries
Testing, adjusting and repair work
Engine operation
Suspended loads
Working on piping and hoses
Work on the Common Rail System
Working on the electric system
Working on the hydraulic system
Electric welding
Painting work
Working with urea solution
Information on how to avoid damage and premature wear
Liability limitation
Shutting down and storage
Regulations for avoiding health and environmental damage
Precautionary measures for protection against health and environmental damage
Disposal of operating utilities and auxiliary operating utilities
Information for working on the diesel engine
Accident protection
Cleanliness
Installation instructions
Engine overhaul
Putting into operation after an engine overhaul
First aid measures
List of abbreviations
Glossary
Glossary used in the Technical Systems documentation for diesel engines
Example: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
01 Engine
0102 Complete component
Complete component
Engine components – right side
Engine components – left side
Engine components – front side
Product Description
Engine Specifications
Identification plates of Perkins 1106D-E70TA diesel engine
Plate Location
Technical specifications Perkins 1106D-E70TA diesel engine
Engine Specifications
General Information
Introduction
0110 Engine housing
Basic engine
Cylinder crankcase
Description of function
Piston, Rings And Connecting Rods
Crankshaft
Viscous Vibration Damper
0120 Cylinder head / Valves / Idler gear
Cylinder head – Valves – Gearwheels drive
Cylinder head
Valve system components
Description of function
Gears and Timing Gear Case
Gear Group (Front) – Time
Crankcase Breather
0125 Injection / Fuel system
Cleanliness of fuel system components
Cleanliness of the engine
Working environment
Tools that have to be used to achieve cleanliness when working on the fuel injection system: Warranty condition.
New Components
Refuelling
Injection system / fuel system
Fuel System
High Pressure Fuel System
Components of the Fuel Injection System
Primary Filter/Water Separator
Secondary Fuel Filter
Fuel Pump Assembly
Typical example of the electrical control system for the fuel system
Fuel Injectors
Fuel Manifold (rail)
0130 Lubricating oil system
Lubricating oil system
Description of function
0135 Cooling system
Cooling System
Coolant Flow
Introduction (Cooling System)
Description of function
0140 Exhaust system
Exhaust system
Air inlet and exhaust system
Description of function
Turbocharger
Turbocharger with wastegate
Wastegate solenoid
0155 Engine control
Starting the diesel engine
Measured values table
Description of function
Perkins speeds table
Diesel engine monitoring system operation
Engine Control System
ECM (A015)
0197 Test/Measurement/Setting
Fuel System – Inspect
Air in Fuel – Test
Tube with visual sight gauge install
Test air bubbles in the fuel
Finding Top Center Position for No. 1 Piston. Fuel Injection Timing – Check
Finding Top Center Position for No. 1 Piston
Timing hole (Camshaft)
Timing hole (Crankshaft)
Fuel Injection Timing – Check
Fuel injection pump install
Fuel Quality – Test
Fuel System – Prime
Prime pump
Air Inlet and Exhaust System – Inspect
Air Inlet Restriction
Air cleaner test
Exhaust Restriction
Exhaust back pressure test
Inspection of the Crankcase Breather
Turbocharger – Inspect
Inspection of the Compressor and the Compressor Housing
Inspection of the Turbine Wheel and the Turbine Housing
Inspection of the Wastegate
Check the Wastegate for Proper Operation
Compression – Test
Glow plugs remove
Aftercooler – Test
Injector Solenoid – Test
Diagnostic Trouble Codes for the Circuit for the Injector Solenoids
Schematic of the circuit for the injector solenoids
P2 ECM connector. View of the pin locations for the injector solenoids
Typical example of the harness connector for the fuel injector solenoids
Typical example of the connector in the cylinder head
Engine Valve Lash – Inspect / Adjust
Cylinder and valve location
Valve Lash Check
Valve Lash Adjustment
Setting the valve lash
Valve mechanism
Engine Oil Pressure – Test
Measuring Engine Oil Pressure
Reasons for Low Engine Oil Pressure
Reason for High Engine Oil Pressure
Engine Oil Pump – Inspect
Oil pump inspect 1
Oil pump inspect 2
Oil pump inspect 3
Excessive Bearing Wear – Inspect
Excessive Engine Oil Consumption – Inspect
Increased Engine Oil Temperature – Inspect
Cooling System – Check (Overheating)
Cooling System – Inspect
Cooling System – Test
Boiling point of water
Checking the Filler Cap
Typical schematic of filler cap
Testing The Radiator And Cooling System For Leaks
Making the Correct Antifreeze Mixtures
Water Temperature Regulator – Test
Water Pump – Inspect
Engine Oil Cooler – Inspect
Engine Oil Cooler with a Low Mounted Filter Base
Vibration Damper – Check
Viscous Vibration Damper
CAN Data Link – Test
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The following background information is relevant for this measure
Typical example of the schematic for the CAN data link
View of the pin locations for the CAN data link on the P1 connector
View of the pin locations for the CAN data link on the P2 connector
Electrical Power Supply – Test
Diagnostic Codes Table
Schematic for the electrical power supply circuit
View of the pin locations on the P1 connector for the ignition keyswitch and battery supply circuit
Schematic for the bypass application harness
Glow Plug Starting Aid – Test
Diagnostic Codes Table
Schematic for the glow plug starting aid circuit
Pin location on the P1 connector for the glow plug starting aid circuit
Ether Starting Aid – Test
Diagnostic Codes Table
Schematic for the Ether starting aid conditions
Schematic diagram for the ether injection solenoid
Terminal locations at the harness connector for the ether solenoid
Pin location on the P1 connector for the ether injection circuit
Solenoid Ether Injection
Sensor Signal (Analog, Active) – Test
Diagnostic Trouble Codes for the Analog, Active Sensors
Schematic for the pressure sensors
Pin locations on the P2 connector for the pressure sensors
Fuel rail pressure sensor
Typical example of an engine pressure sensor
Sensor Signal (Analog, Passive) – Test
Diagnostic Trouble Codes for the Analog, Passive Sensors
Schematic for the (Analog, Passive) sensors
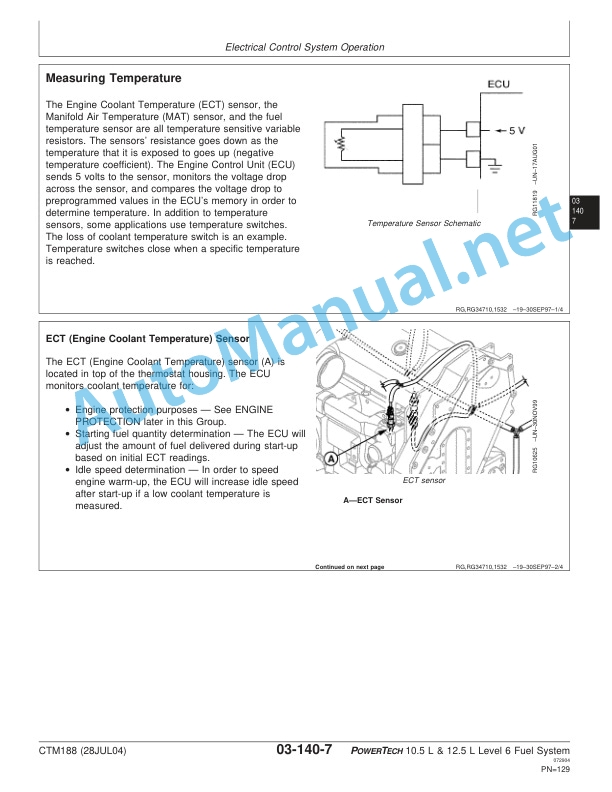
P2 pin locations for the temperature sensors
Typical view of an engine temperature sensor
Sensor Supply – Test
Sensor power supply diagnostic trouble codes
Typical example of the 5 VDC supply circuit
Typical example of the 8 VDC supply circuit
Pin locations on the P1 connector for the sensor supply circuits
Pin locations on the P2 connector for the sensor supply circuits
Fuel rail pressure sensor
Typical example of an engine pressure sensor
Typical example of a speed/timing sensor
Solenoid Valve – Test
Diagnostic trouble codes
Schematic for the solenoid valves
Pin locations on the P2 connector for the solenoid valves
Speed/Timing – Test
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Description
Schematic for the speed/timing sensor
Typical example of a speed/timing sensor
Pin locations for the speed/timing sensor on the P2 connector
Water in Fuel – Test
Water-in-Fuel Sensor Operation
Schematic for the WIF sensor
Pin locations on the P1 connector for the WIF sensor
Connector for the WIF sensor
Electrical Connectors – Inspect
Connector Illustration. Detail A
Diagram for the installation of a connector plug (typical example)
Seal for a three-pin connector
Seal for the ECM connector
A typical example of the lock wedge.
Diagram for testing pin retention
Replacing the engine control module (ECM)
Configuration Parameters
Codes That Relate to Configuration Parameters
Function Description
ECM Software – Install (Flash programming)
Codes That Relate to Configuration Parameters
Function Description
0198 Problem / Remedy
Coolant contains oil
Introduction
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Coolant Level Is Low
Introduction
Coolant temperature is high
Introduction
Diagnostic trouble codes for high coolant temperature
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Cylinder is noisy
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine cranks but does not start
Probable Causes
Recommended actions
Engine does not crank
Probable Causes
Recommended Repairs
Engine Has Early Wear
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Has Mechanical Noise (Knock)
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Misfires, Runs Rough or is Unstable
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Overspeeds
Diagnostic Trouble Code for Engine Overspeed
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Shutdown Occurs Intermittently
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Stalls at Low RPM
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Top Speed is Not Obtained
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Engine Vibration Is Excessive
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Exhaust Has Excessive Black Smoke
Probable causes
Recommended Actions
Exhaust Has Excessive White Smoke
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Fuel Consumption Is Excessive
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Fuel Contains Water
Recommended actions
Fuel Rail Pressure Problem
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Inlet Air is Restricted
Inlet Air Temperature Is High
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Intake Manifold Air Pressure Is High
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Intake Manifold Air Pressure Is Low
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Intake Manifold Air Temperature Is High
Probable Causes
Recommended Actions
Oil Consumption is Excessive
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Oil Contains Coolant
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Oil Contains Fuel
Measuring Fuel Dilution
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Oil Pressure is Low
Diagnostic codes for low engine oil pressure
Diagnostic code 100-17 Engine Oil Pressure versus Engine Speed
Diagnostic code 100-1 Engine Oil Pressure versus Engine Speed
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Power is Intermittently Low or Power Cutout is Intermittent
Probable causes
Recommended actions
Valve Lash is Excessive
Probable causes
Recommended actions
10 Electrical / Electronic equipment
1012 Modules / sensors
Module A015 – PERKINS 1106D – E70TA (System Overview)
System Overview
Module A015 – (ECM) Engine Control Module
Sensors / actuators – PERKINS 1106D – E70TA
Sensor Locations for the Engine
Sensor locations on the left side of the engine
Close view of Sensors on the left side of the engine
Sensor locations on the right side of engine
Speed/Timing Sensors
Primary speed/timing sensor
Secondary speed/timing sensor
Schematic for the speed/timing sensor
Pressure Sensors
Schematic for the pressure sensors
Temperature Sensors
Schematic for the engine temperature sensors
Engine Harness
92 Diagnosis
9220 Error codes engine (J1939)
FMI failure code (Failure Mode Indicator)
FMI fault code (Failure Mode Indicator) PERKINS
FMI 00 (Signal too high)
FMI 01 (Signal too low)
FMI 02 (Erratic signal)
FMI 03 (Voltage too high)
FMI 04 (Voltage too low)
FMI 05 (Current too low)
FMI 06 (Current too high)
FMI 07 (Mechanical fault)
FMI 08 (Faulty frequency signal)
FMI 09 (Communication fault)
FMI 10 (Signal changes too quickly)
FMI 11 (Multiple fault)
FMI 12 (ECU defective)
FMI 13 (Signal outside of calibration range)
FMI 16 (Parameter not available)
FMI 17 (No reply from ECU)
FMI 18 (Power supply fault)
FMI 19 (Software conditions not met)
Fault codes
Diesel engine fault codes – J 1939 / PERKINS / 1106D – E70TA
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Event Codes
9295 Measuring devices
Connecting CDS
Home screen after communication with the CDS
CDS features
Module overview
Engine control
Connecting CDS
Module diagnostics
Engine tests (Example only)
GENERAL 1: How to find the engine tests
GENERAL 2: Selection menu (engine tests)
Injector solenoid test (0125)
Test description
Cylinder Cutout Test (0155)
Test description
Test Module Outputs (0155)
Setting of Module Outputs and Valves
Position of components
Electric system
A Terminal / modules
B Sensors
Y Solenoid coils
00 0302 565 2.pdf:
Sensor system
Table of contents
CCN explanation
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
Electric system standard
Overview
Hydraulic system standard
Overview
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
Introduction
Safety rules
Safety and hazard information
10 Electrical / Electronic equipment
1097 Testing / Measuring / Adjusting
Test report of the angle sensor (0011780.x)
Application of test report
Required tools
Test report of the angle sensor (0011780.x)
Testing / Measuring / Adjusting of angle sensor (0011780.x)
1. Reason for test
2. Mechanical test of angle sensor
3. Electric test with CDS
4. Electric test with multimeter
5. Mechanical test of connecting cable
Completing the machine
Test report of position and speed sensors
Application of test report
Required tools
Sensor variants
Part numbers of speed sensors
Part number of position sensor
Test report of position and speed sensors
Testing / measuring / adjusting of position and speed sensors
1. Reason for test
2. Mechanical test
3. Electric test with CDS
4a. Installation dimensions
Check of installation dimension
Installation dimensions of gearbox speed sensor (0011 799.x) and cam speed sensor (0011 810.x)
Installation dimension of position sensor (0011 815.x)
4b. Installation position
Centring of sensor
Metal-free zone
5. Electric test with multimeter
Voltage measurement
Direction of rotation and speed sensor (0011 605.x)
Measured values table
6. Mechanical test of connecting cable
Completing the machine
Test report of the urea sensor (00 0773 207 x)
Application of test report
Required tools
Parts number of the urea sensor
Test report of the urea sensor
Testing / measuring / adjusting urea sensor
1. Reason for test
2. Mechanical test
3. Mechanical test of connecting cable
4. Electric test with multimeter
5. Component test with the CDS
00 0302 594 1.pdf:
DOMINATOR 370
Table of contents
Introduction
Safety rules
Safety and hazard information
Validity of manual
Validity of manual
CCN explanation
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
Electric systems standard
Overview
Hydraulic system standard
Overview
CCN (CLAAS Component Number)
01 Engine
0150 Engine attachment parts
Starting the diesel engine
Description of function
Perkins speed table
0155 Engine control
Diesel engine monitoring
Measured values table
Description of function
03 Chassis
0330 Driven steering axle, rear
Description of function
0335 Ground drive
Hydrostatic ground drive
Description of function
Pump unit (HPV)
Description of function
Servo-control valve
Description of function
Multifunction valve (7013/7014)
Description of function
Ground drive fixed-displacement motor (HMF)
Description of function
05 Steering
0505 Steering
Steering system – General
Neutral function diagram
Function diagram with steering actuated
09 Hydraulic system
0910 Pumps
Ground drive variable-displacement pump
Key to diagram
0920 Valves
Main valve
Working hydraulics valve block
Front attachment dampening valve block
Steering (Orbitrol) valve block
Low-pressure hydraulics valve block
Reel drive valve block
Hydraulic system thermostat
0930 Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinder – variants of end position venting
Description of function
0980 Hydraulic circuit diagram
Machine circuit diagram
Front attachment hydraulics circuit diagrams
Cutterbar C370-C490 (type 527) – Reel adjustment
VARIO cutterbar V540-V900 (type 716) – Reel adjustment
VARIO cutterbar V540-V1050 (type 716) – Rape cutter drive
Folding cutterbar 450-540 (type 713)
10 Electrical / Electronic equipment
1010 Central electrics
Basic central terminal compartment
Fuse assignment
Relay assignment
1012 Modules / sensors
Module A008 – AUTO CONTOUR (CAC)
Module pin assignment A008 – AUTO CONTOUR (CAC)
Module A015 – engine control unit TIER3
Module A015 – engine control unit TIER3
Module A069 – vehicle base module (VBM)
Key to diagram
Key to diagram
Module A183 – vehicle base module 2 (VBM2)
Key to diagram
Key to diagram
1035 Operation / Multifunction control lever
T signal function
Measured values table
Description of function
Road travel – fieldwork circuit function
Description of function
1080 Electronic circuit diagram
Introduction into circuit diagrams
Overview of designations
CLAAS cable marking
Wire colours
Power supply
Actuators
Actual value switch (output = 0 or 1)
Internal connections
Overview of CAN Bus system
Communication
Standards
Electric circuit diagrams of machine (SCM)
SCM 01 – Multicoupler
SCM 02 – Electric power supply – Starting the diesel engine
Key to diagram
SCM 03 – Power supply of modules
Key to diagram
SCM 04 – Road travel
Key to diagram
SCM 05 – Threshing mechanism
Key to diagram
SCM 06 – Power supply of sensors
Key to diagram
SCM 07 – Earth supply
SCM 08 – CAN0 (Vehicle CAN) / CAN1 (J1939-CAN)
Key to diagram
SCM 09 – CAN2 (Front CAN) / CAN5 (ISO Bus CAN)
Key to diagram
SCM 10 – Diesel engine speed adjustment – Diesel engine control unit
Key to diagram
SCM 11 – Diesel engine monitoring
Key to diagram
SCM 12 – Front clutch engagement – Front attachment reverse
Key to diagram
SCM 13 – Raise / lower front attachment – CAC
Key to diagram
SCM 15 – Reel speed adjustment
Key to diagram
SCM 16 – Reel adjustment
Key to diagram
SCM 19 – Circulation lock valve, hydraulic system monitoring
Key to diagram
SCM 20 – Speed monitoring
Key to diagram
SCM 21 – Threshing mechanism speed adjustment
Key to diagram
SCM 22 – Fan speed adjustment
Key to diagram
SCM 23 – Machine monitoring
Key to diagram
SCM 25 – Swinging the grain tank unloading tube in/out / grain tank unloading
Key to diagram
SCM 26 – Grain tank full indicator / warning beacons
Key to diagram
SCM 27 – Brake light
Key to diagram
SCM 28 – Back-up horn
Key to diagram
SCM 29 – Air conditioner
Key to diagram
SCM 30 – Windscreen wiper / windscreen washer
Key to diagram
SCM 31 – Light / side lights main circuit
Key to diagram
SCM 32 – Drive lights
Key to diagram
SCM 33 – Main work light circuit
Key to diagram
SCM 34 – Grain tank work light / returns / sieve pan
Key to diagram
SCM 35 – Turn flasher light
Key to diagram
SCM 36 – Instrument lighting
Key to diagram
SCM 37 – Cab equipment
Key to diagram
SCM 38 – Service sockets
Key to diagram
SCM 44 – Rear wheel position indicator
Key to diagram
SCM 46 – Warning lights
Key to diagram
SCM 49- Diesel engine CAN
Key to diagram
SCM 51 – Engine TIER3
Key to diagram
Front attachment circuit diagrams – soybean cutterbar (type 440)
T440 01 – Multi-coupling
Key to diagram
T440 02 – Reel
Key to diagram
T440 03 – AUTO CONTOUR
Key to diagram
T440 04 – Lighting
Key to diagram
T440 05 – AUTO PILOT
Key to diagram
Front attachment circuit diagrams – standard cutterbar (type 527)
T527 01 – Multi-coupling
Key to diagram
T527 02 – Reel
Key to diagram
T527 03 – AUTO CONTOUR
Key to diagram
T527 04 – AUTO PILOT
Key to diagram
Front attachment circuit diagrams – folding cutterbar (type 713)
T713 01 – Multi-coupling
Key to diagram
T713 02 – Reel
Key to diagram
T713 03 – Folding the front attachment
Key to diagram
T713 04 – AUTO CONTOUR
Key to diagram
T713 05 – Lighting
Key to diagram
T713 06 – AUTO PILOT
Key to diagram
Front attachment electric circuit diagrams – standard cutterbar (type 715)
T715 01 – Multi-coupling
Key to diagram
T715 02 – Reel
Key to diagram
T715 03 – Rape cutter
Key to diagram
T715 04 – AUTO CONTOUR
Key to diagram
T715 05 – AUTO PILOT
Key to diagram
Front attachment electric circuit diagrams – Vario cutterbar (type 716)
T716 00 – Overview of modules
Key to diagram
T716 01 – Multi-coupling
Key to diagram
T716 02 – Power supply of modules / CAN Bus
Key to diagram
T716 03 – Reel
Key to diagram
T716 04 – Cutting table adjustment
Key to diagram
T716 05 – Rape cutter
Key to diagram
T716 06 – AUTO CONTOUR
Key to diagram
T716 07 – AUTO PILOT
Key to diagram
1081 Overview of Connectors
Connector database (CHP CLAAS)
Example of representation of key numbers (CHP)
Connector representation (CHP)
1085 Networks
BUS systems (CAN) – Basic machine
Description of function
1097 Testing / Measuring / Adjusting
12 Cab / Operator’s platform
1230 Seat
Seat contact
Description of function
20 Crop feeding
2002 Front attachment
Raising / lowering the front attachment
Measured values table
Description of function
Front attachment ON / OFF
Description of function
Function not actuated (S055 in rest position)
Front attachment ON
Front attachment OFF
Important:
Reverse front attachment
Description of function
Front attachment dampening
Measured values table
Description of function
2015 Reel / Crop guard
Raise/lower reel
Reel adjustment function description
Reel speed adjustment
Reel adjustment function description
26 Ground guidance
2697 Testing / Measuring / Adjusting
Pressure accumulator adjustment
Accumulator pressure filling instructions
41 Threshing mechanism
4100 Threshing mechanism
Threshing mechanism ON/OFF
Description of function
4120 Threshing drum
Threshing drum speed adjustment
Measured values table
Description of function
43 Cleaning system
4325 Cleaning fan
Fan speed adjustment
Description of function
61 Grain delivery
6110 Grain tank
Grain tank fill indicator
Description of function
6120 Grain tank unloading
Grain tank unloading
Description of function
Swinging the grain tank unloading tube
Description of function
92 Diagnosis
9210 Error codes machine
FMI fault codes
FMI 00 (signal too high)
FMI 01 (signal too low)
FMI 02 (erratic signal)
FMI 03 (voltage too high)
FMI 04 (voltage too low)
FMI 05 (current too low)
FMI 06 (current too high)
FMI 07 (mechanical fault)
FMI 08 (faulty frequency signal)
FMI 09 (communication fault)
FMI 10 (signal change too fast)
FMI 11 (multiple faults)
FMI 12 (ECU defective)
FMI 13 (signal outside of calibration range)
FMI 16 (parameter not available)
FMI 17 (ECU does not respond)
FMI 18 (power supply fault)
FMI 19 (software conditions not met)
FMI 95 (no signal change)
FMI 96 (CAN BUS system defective)
FMI 97 (erratic status)
FMI 98 (warning)
FMI 99 (Info)
Machine fault code list (DTC)
DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) overview
Position of components
Hydraulic system
1000 Oil reservoir / oil filter / oil cooler
2000 Pump / motor
3000 Hydraulic cylinders
5000 Accumulators
7000 Valves – hydraulically actuated
9000 Measuring points / gauges
Electric system
A Terminal / modules
B Sensors
C Electrical / electronic devices
E Lighting
G Voltage sources
H Signal device / light
K Relays
M Motor (electric)
S Switches / pushbuttons – cab operation
U Switch – External operation
Y Solenoid coils
Z Actual value switch
CHP-numbers for connectors CLAAS HARNESS PARTS.pdf:
CLAAS HARNESS PARTS
Table of contents
10 Electrical / Electronic equipment
1081 Overview of connectors
CLAAS HARNESS PARTS (CHP)
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
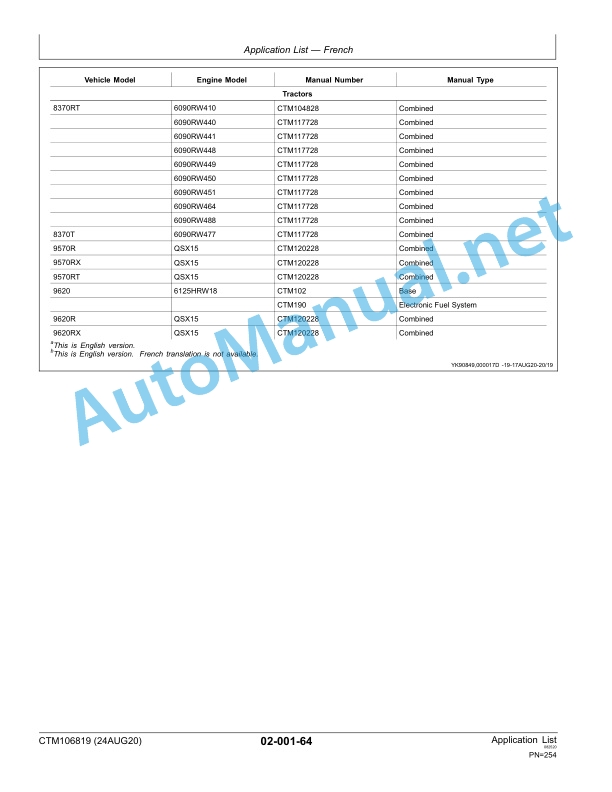
John Deere Application List Component Technical Manual CTM106819 24AUG20
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere DF Series 150 and 250 Transmissions (ANALOG) Component Technical Manual CTM147 05JUN98
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere POWERTECH E 4.5 and 6.8 L Diesel Engines TECHNICAL MANUAL 25JAN08
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Parts Catalog PDF
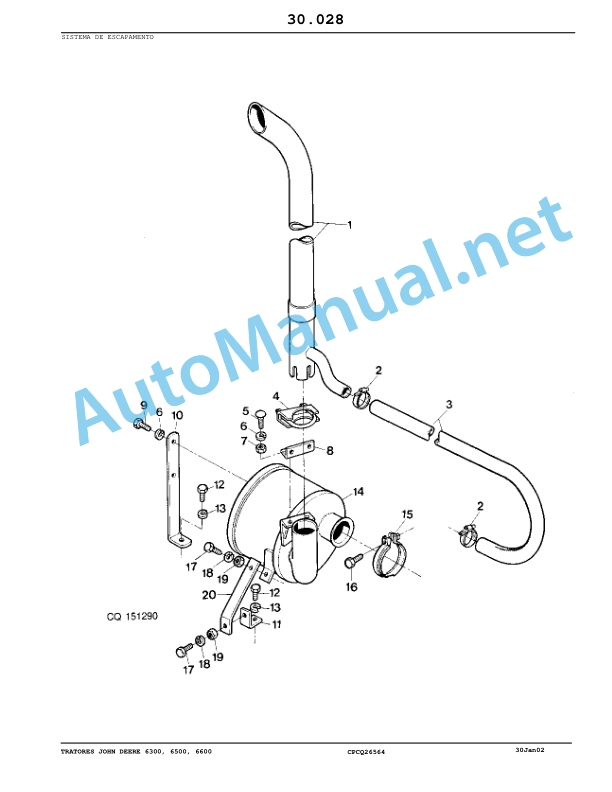
John Deere Tractors 6300, 6500, and 6600 Parts Catalog CQ26564 (29SET05) Portuguese
- Claas
- Grove
- New Holland
- Komatsu
- Kubota
- John Deere
- Linde
- Bomag
- CASE
- Clark
- JCB
- Jungheinrich
- Linde
- Yale
- Yanmar
- Manitou
- Manitowoc
- CNH
- Doosan
- Fiatagri
- Fiatallis
- Fiatallis Other Manual PDF
- Flexi Coil
- Ford New Holland
- Ford New Holland Other Manual PDF
- Huyndai
- Hypac
- Hyster
- Hyster Service Manual PDF
- Isuzu
- Kobelco
- Kohler
- Krupp
- Lombardini
- Mahindra
- Nuvera
- Perkins
- Sperry New Holland
- Utilev
- Versatile
- ZF