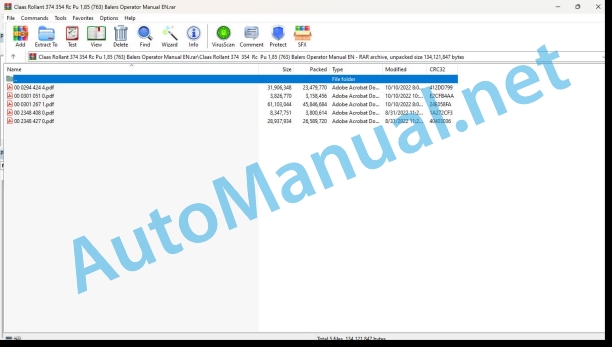
Claas Rollant 374 354 Rc Pu 1,85 (763) Balers Operator Manual EN
$50.00
- Model: Rollant 374 354 Rc Pu 1,85 (763) Balers
- Type Of Manual: Operator Manual
- Language: EN
- Format: PDF(s)
- Size: 98.1 MB
File List:
00 0294 424 4.pdf
00 0301 051 0.pdf
00 0301 267 1.pdf
00 2348 408 0.pdf
00 2348 427 0.pdf
00 0294 424 4.pdf:
ROLLANT 354 RotoFeed
ROLLANT 354 RotoCut
ROLLANT 355 RotoCut
Table of contents
1 To this operator’s manual
1.1 General Information
1.1.1 Manual validity
1.1.2 Using the manual
1.1.3 Technical specifications
2 Safety
2.1 General Information
2.1.1 General points
2.1.2 Using in line with intended usage
2.1.3 Reasonably foreseeable improper usage
2.1.4 Driving on the road
2.1.5 Definition of hazard information
2.1.6 Safety advice
2.1.7 Accident prevention
2.1.8 Waste disposal
2.1.9 Residual risks
2.2 Safety decals
2.2.1 Description
2.2.2 Location of safety stickers
2.3 Safety equipment
2.3.1 Indicator lights
2.3.2 Reflective equipment
2.3.3 Chocks
2.3.4 Retaining cable (machine not equipped with brake and which can be used in France)
2.3.5 Parking brake
2.3.6 Jack stand
2.3.7 Locking the tailgate
2.3.8 Locking the pick-up
2.3.9 Extinguisher
3 Machine description
3.1 Existing models
3.1.1 Machine description
3.2 Overview and functions
3.2.1 Left-hand side
3.2.2 Right-hand side
3.2.3 Roller identification
3.3 Working and service areas
3.3.1 General points
3.3.2 Front section of the baler
3.4 Name plate and serial number
3.4.1 Replacement parts and technical information
3.4.2 Identification number
3.4.3 Machine identification plate
3.4.4 Drawbar identification plate (depending on equipment)
3.4.5 Axle identification plate (depending on equipment)
3.5 General operating principle
3.5.1 Baling cycle
3.6 Control terminal
3.6.1 Control terminal
3.6.2 ISOBUS connection
3.7 Transmission and drive
3.7.1 Power transmission
3.7.2 Main drive
3.7.3 Pick-up drive
3.7.4 Rotor drive (optional)
3.7.5 Drive chains
3.8 Crop feeding
3.8.1 Pick-up
3.8.2 Crop guard
3.8.3 Short crop plate (optional)
3.8.4 Roller crop press (optional)
3.9 Feeder unit
3.9.1 Rotor
3.9.2 RotoCut cutting unit (optional)
3.9.3 Automatic RotoCut knife cleaning (optional)
3.9.4 Manual rotor reverse (optional)
3.9.5 Hydraulic rotor reverse (optional)
3.10 Baling system
3.10.1 Bale chamber and rollers
3.10.2 Baling cycle
3.11 Tying system
3.11.1 Tying categories and types
3.11.2 Standard tying
3.11.3 Comfort tying
3.11.4 Tying settings
3.11.5 Twine box (depending on equipment)
3.11.6 Spare net storage (depending on equipment)
3.11.7 Net box (depending on equipment)
3.12 Bale discharge
3.12.1 Bale chute
Use without the bale chute
3.13 Central lubrication
3.13.1 Automatic chain lubrication
3.13.2 Manual central lubrication (optional)
3.13.3 Automatic central lubrication (optional)
3.14 Brake
3.14.1 General points
3.14.2 Hydraulic brakes
3.14.3 Active hydraulic brakes
3.14.4 Pneumatic brakes
3.15 Hydraulic system
3.15.1 Baler hydraulic unit
3.15.2 Continuous hydraulic circulation
3.16 Equipment
3.16.1 Ladder (depending on equipment)
3.16.2 Step
3.16.3 Pressure gauge
3.16.4 Electronic module
4 Operating and control elements
4.1 General Information
4.1.1 Control terminal
4.1.2 ISOBUS connection
4.2 CLAAS Medium Terminal
4.2.1 Presentation
4.2.2 Screen
4.2.3 Key identification
4.2.4 Home page
4.2.5 Description of the CLAAS Medium Terminal Menus
4.3 CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
4.3.1 Presentation
4.3.2 General points
4.3.3 Screen
4.3.4 Key identification
4.3.5 Description of the General menu of the CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
4.3.6 Description of the Use menu of the CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
4.3.7 Description of the CLAAS COMMUNICATOR Service menus
4.4 ISOBUS terminal
4.4.1 Presentation
4.4.2 General points
5 Technical specifications
5.1 Baler
5.1.1 Dimensions
5.1.2 Weight
5.1.3 Hitching
5.1.4 Universal drive shaft
5.1.5 Feeding and baling
5.1.6 Tying device
5.1.7 Wheels
5.1.8 Hydraulic circuit
5.1.9 Bolt tightening torques
5.1.10 Braking
5.1.11 Greasing and lubrication
5.1.12 Noise level
5.2 Safety devices
5.2.1 Shear bolts
5.2.2 Torque limiter
5.3 Tractor
5.3.1 Power required
5.3.2 Hitching
5.3.3 Power take-off
5.3.4 Electrical connections
5.3.5 Hydraulic connections
5.3.6 Hydraulic oil and circuit
5.3.7 Braking
6 Machine preparation
6.1 General Information
6.1.1 Before first use
6.1.2 Checking the equipment
6.2 Universal drive shaft
6.2.1 Safety advice
6.2.2 Overlap of the universal drive shaft
6.2.3 Adapting the length of the universal drive shaft
6.2.4 Fitting the universal drive shaft
6.3 Coupling frame
6.3.1 Recommendations
6.3.2 Coupling types
6.3.3 Adapting jaw drawbar/swinging drawbar
6.3.4 Fitting the universal drive shaft
6.3.5 Retaining cable (machine not equipped with brake and which can be used in France)
6.4 Hydraulic connections
6.4.1 Identifying the hydraulic hoses
6.4.2 With CLAAS Medium Terminal
6.4.3 With CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
6.5 Electrical connections
6.5.1 Identifying the electrical cables
6.5.2 Lighting
6.5.3 Battery cable (optional)
6.5.4 Electrical supply for the baler and the CLAAS Medium Terminal
6.5.5 Electrical supply for the baler and the CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
6.5.6 Electrical supply for the baler using the ISOBUS cable
6.6 Brake
6.6.1 Hydraulic brakes
6.6.2 Active hydraulic brakes
6.6.3 Pneumatic brake
6.7 Twine tying
6.7.1 Preparation
6.7.2 Adjusting the twine tensioner
6.7.3 Fitting the twine
6.7.4 Fitting the side stop for the twine
6.7.5 Selecting standard twine tying
6.7.6 Selecting comfort twine tying
6.8 Net tying
6.8.1 Preparation
6.8.2 Fitting the net
6.8.3 Adjusting the net brake
6.8.4 Selecting standard net tying
6.8.5 Selecting comfort net tying
6.9 Bale discharge
6.9.1 Fitting the bale discharge chute
6.9.2 Pre-setting the bale discharge chute
6.10 Baling chamber
6.10.1 Bale starting stops
6.10.2 Setting the MPS
6.11 Cutting unit
6.11.1 Safety advice
6.11.2 Checking
6.11.3 Fitting the knives
6.11.4 Fitting the dummy knives (optional)
6.11.5 Unused knives and dummy knives
6.12 Loading the machine
6.12.1 Lashing the baler
6.12.2 Lifting points
6.12.3 Lifting
7 Operation
7.1 General Information
7.1.1 Baler user
7.1.2 Side doors
7.2 Travelling with the baler
7.2.1 Checking the equipment
7.2.2 Preparing for transportation
7.2.3 Travelling on the road
7.2.4 Arriving at the field
7.2.5 Driving in fields
7.2.6 Parking
7.3 Before each usage
7.3.1 Universal drive shaft
7.3.2 Reminders
7.3.3 Baler maintenance
7.3.4 Checking the equipment
7.4 Commissioning in the field
7.4.1 User advice
7.4.2 Starting the machine
Machine equipped with CLAAS Medium Terminal
Machine equipped with CLAAS COMMUNICATOR or an ISOBUS connection
7.5 Pick-up
7.5.1 Important
7.5.2 Pick-up wheels
7.5.3 Pick-up height
7.5.4 Crop guard
7.6 Tying
7.6.1 Selecting twine or net tying (optional)
7.6.2 Setting the number of twine wraps
Machine equipped with standard tying
Machine equipped with comfort tying
7.6.3 Setting the number of net wraps
Machine equipped with standard tying
Machine equipped with comfort tying
7.7 Bale parameters
7.7.1 Bale settings
7.8 CLAAS Medium Terminal
7.8.1 Sound
7.8.2 Selecting twine or net tying (optional)
7.8.3 Resetting the day counter
7.8.4 Counters Menu
7.8.5 Tying delay
7.8.6 Baling/tying process
Baling-tying process steps
7.8.7 Manually activating the tying process
7.8.8 Tying process manual delay
7.8.9 RotoCut cutting unit (optional)
7.8.10 Faults
7.9 CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
7.9.1 Counter menu
Job selection and settings
7.9.2 Selecting twine or net tying (optional)
7.9.3 Usage parameter settings
Settings
7.9.4 Softkeys
7.9.5 Pick-up
7.9.6 Cylinder pressure recharge from the first bale
7.9.7 RotoCut cutting unit
7.9.8 Manually activating the tying process
Anticipated tying start
Tying delay
7.9.9 Baling / tying process
Net tying
Twine tying
Baling-tying process steps
7.9.10 Faults
7.9.11 Baler Diagnostic sub-menu
7.10 ISOBUS terminal
7.10.1 General points
7.11 Unblocking the baler
7.11.1 How can blockages be avoided?
7.11.2 Safety advice
7.11.3 Unblocking the pick-up
7.11.4 Unblocking the rotor (baler equipped with CLAAS Medium Terminal)
7.11.5 Unblocking the rotor (baler equipped with CLAAS COMMUNICATOR)
7.12 After use
7.12.1 Reminders
7.12.2 Securing the baler
7.12.3 Daily cleaning
7.12.4 Unhitching the baler
8 Faults and remedies
8.1 General Information
8.1.1 Sensors
8.2 CLAAS Medium Terminal
8.2.1 General points
8.2.2 Electric circuit
8.2.3 Bale discharge
8.2.4 Twine tying
8.3 CLAAS COMMUNICATOR
8.3.1 General points
8.3.2 Electric circuit
8.3.3 Bale discharge
8.3.4 Net tying
8.3.5 Twine tying
8.3.6 Twine knife
8.4 Tying system
8.4.1 Cause of the faults
8.4.2 Net tying
8.4.3 Twine tying
8.5 Lubricating oil system
8.5.1 Cause of the problems
8.5.2 Resolving faults
8.5.3 Central lubrication
8.6 Other functions
8.6.1 General points
8.6.2 General functions
9 Maintenance
9.1 General maintenance Information
9.1.1 Maintenance and safety advice
9.1.2 Wheels and tyres
9.1.3 Brakes
9.1.4 Hydraulic circuit
9.1.5 V-belt
9.1.6 Chains
9.1.7 Baling/tying device
9.1.8 Hitching
9.1.9 Universal drive shaft
9.1.10 Cutting unit
9.1.11 Safety device
9.1.12 Nuts and bolts
9.1.13 Lubricants and lubricating
9.1.14 Inductive sensors
9.1.15 Welding work
9.1.16 Replacement parts
9.2 Maintenance schedules
9.2.1 Maintenance operations before gathering crop
9.2.2 Maintenance operations after the first 10 hours of operation
9.2.3 Maintenance operations after the first 50 hours of operation
9.2.4 Maintenance operations every 8 hours of operation or every day
9.2.5 Maintenance operations every 50 hours of operation
9.2.6 Maintenance operations every 100 hours of operation
9.2.7 Maintenance operations every 250 hours of operation
9.2.8 Maintenance operations, annual or every 500 hours of operation
9.2.9 Maintenance operations if necessary
9.3 Lubricants charts
9.3.1 Lubricants
9.4 Lubrication chart
9.4.1 Lubricating
9.4.2 Lubrication points – 8 h
9.4.3 Lubrication points – 50 h
9.4.4 Lubrication points – 100 h
9.4.5 Lubrication points – 250 h
9.5 Maintenance operations gearbox
9.5.1 540 rpm drive gearbox
9.5.2 1,000 rpm drive gearbox
9.5.3 Universal drive shaft shear bolt
Replacing the bolt
9.6 Maintenance operations axle and wheels
9.6.1 Checking the tyres
9.6.2 Checking the wheel tightness
9.6.3 Changing the wheels
9.6.4 Wheel hub
9.7 Maintenance operations brake
9.7.1 Hydraulic and active hydraulic brakes
9.7.2 Pneumatic brakes
9.7.3 Replacing the brake pads
9.8 Maintenance operations hitch
9.8.1 Hitch coupling and drawbar mounting
9.9 Maintenance operations hydraulic system
9.9.1 Filter
9.10 Pick-up maintenance operations
9.10.1 Pick-up drive chains
9.10.2 Pick-up shear bolt
9.10.3 Pick-up tensioner
9.11 Maintenance work feeder unit
9.11.1 Rotor drive spring
9.11.2 Setting the knife height (RotoCut Machines)
9.11.3 Rotor reverser unit shear bolt (optional)
9.12 Maintenance operations baling chamber
9.12.1 MPS springs (oscillating segment)
9.12.2 Roller drive springs
9.12.3 Cleaning the roller
9.13 Maintenance operations tying
9.13.1 Twine tying
9.13.2 Net tying
9.14 Maintenance operations bale discharge
9.14.1 Bale discharge chute
9.15 Maintenance operations central lubrication system
9.15.1 Chain lubrication
9.15.2 Manual central bearing lubrication (optional)
9.15.3 Automatic central bearing lubrication (optional)
9.16 Maintenance operations machine body
9.16.1 Extinguisher (optional)
9.17 Winter storage
9.17.1 General points
9.17.2 Cleaning
9.17.3 Lubricating
9.17.4 Maintenance
9.17.5 Storage
10 Placing out of operation and disposal
10.1 General Information
10.1.1 Removal from service and disposal
11 EC-declaraction of conformity
11.1 General Information
11.1.1 EC Declaration of conformity
00 0301 051 0.pdf:
PROFI CAM 3
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Notes on the manual
1.1.1 Validity of manual
1.1.2 Information about this Operator’s Manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.1.4 Optional equipment
1.1.5 Qualified specialist workshop
1.1.6 Maintenance information
1.1.7 Warranty notes
1.1.8 Spare parts and technical questions
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Intended use
1.2.2 Reasonably foreseeable misuse
2 Safety
2.1 Identifying warnings
2.1.1 Hazard signs
2.1.2 Signal word
2.2 Safety rules
2.2.1 Meaning of Operator’s Manual
2.2.2 Observing safety decals and warnings
2.2.3 Optional equipment and spare parts
3 Product description
3.1 Overview and method of operation
3.1.1 How the PROFI CAM works
3.2 Identification plates and identification number
3.2.1 Position of identification plates
3.2.2 Explanation of PROFI CAM identification plate
3.3 Information on the product
3.3.1 CE marking
4 Operating and control elements
4.1 Camera system
4.1.1 Camera system monitor
4.2 Menu structure
4.2.1 Main menu
4.2.2
4.2.3
4.2.4
4.2.5
4.2.6
5 Technical specifications
5.1 PROFI CAM
5.1.1 Monitor
5.1.2 Camera
5.1.3 Switch box
5.1.4 Degree of protection against foreign bodies and water
6 Preparing the product
6.1 Shutting down and securing the machine
6.1.1 Switching off and securing the machine
6.2 Prior to operation
6.2.1 Carry out prior to operation
6.2.2 Installing the sun protection
6.2.3 Aligning the camera
6.2.4 Connecting the camera electrics
7 Operation
7.1 Monitor
7.1.1 Switching on the monitor
7.1.2 Calling up the menu
7.1.3 Setting a menu item
7.1.4 Setting the image orientation
7.1.5 Setting automatic screen darkening
7.1.6 Image mirroring
7.1.7 Setting the trigger view
7.1.8 Setting the follow-up time for trigger view
7.1.9 Setting the display mode
7.1.10 Activating/deactivating a display mode
8 Faults and remedies
8.1 Electrical and electronic system
8.1.1 Overview of problems on PROFI CAM camera system
8.1.2 Replacing the switch box fuse
9 Maintenance
9.1 Maintenance intervals
9.1.1 Every 10 operating hours or daily
9.2 Camera system
9.2.1 Checking the camera system for dirt
9.2.2 Cleaning the camera
9.2.3 Cleaning the switch box
9.2.4 Cleaning the monitor
10 Placing out of operation and disposal
10.1 General Information
10.1.1 Putting out of operation and disposal
11 Technical terms and abbreviations
11.1 Abbreviations
11.1.1 Units
11.1.2 Abbreviations
11.1.3 Technical terms
00 0301 267 1.pdf:
ROLLANT 374 RotoFeedROLLANT 374 RotoCutROLLANT 375 RotoCut
Table of contents
1 To this Operator’s Manual
1.1 General information
1.1.1 Manual validity
1.1.2 Using the manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.1.4 Technical specifications
2 Safety
2.1 General information
2.1.1 General points
2.1.2 Using in line with intended usage
2.1.3 Reasonably foreseeable improper usage
2.1.4 Driving on the road
2.1.5 Definition of hazard information
2.1.6 Safety advice
2.1.7 Accident prevention
2.1.8 Waste disposal
2.1.9 Residual risks
2.2 Safety decals
2.2.1 Description
2.2.2 Location of safety stickers
2.3 Safety equipment
2.3.1 Indicator lights
2.3.2 Reflective equipment
2.3.3 Chocks
2.3.4 Retaining cable (machine not equipped with brake and which can be used in France)
2.3.5 Parking brake
2.3.6 Jack stand
2.3.7 Locking the tailgate
2.3.8 Locking the pick-up
2.3.9 Extinguisher
3 Machine description
3.1 Existing models
3.1.1 Machine description
3.2 Overview and functions
3.2.1 Left-hand side
3.2.2 Right-hand side
3.2.3 Roller identification
3.3 Working and service areas
3.3.1 General points
3.3.2 Front part of the baler
3.4 Identification plate and serial number
3.4.1 Replacement parts and technical information
3.4.2 Position of identification plates
3.4.3 Machine identification plate
3.4.4 Drawbar identification plate
3.5 General operating principle
3.5.1 Baling cycle
3.6 Control terminal
3.6.1 Control terminal
3.6.2 ISOBUS connection
3.6.3 EASY on board
3.7 Transmission and drive
3.7.1 Power transmission
3.7.2 Main drive
3.7.3 Pick-up drive
3.7.4 Rotor drive
3.7.5 Drive chains
3.8 Crop feeding
3.8.1 Pick-up
3.8.2 Crop guard
3.8.3 Short crop plate (optional)
3.8.4 Roller crop press (optional)
3.9 Feeder unit
3.9.1 Rotor
3.9.2 Rotor chassis with pivoting floor (option)
3.9.3 RotoCut cutting unit (optional)
3.9.4 Automatic RotoCut knife cleaning (optional)
3.9.5 Manual rotor reverse*
3.10 Baling system
3.10.1 Bale chamber and rollers
3.10.2 Baling cycle
3.11 Tying system
3.11.1 Tying categories and types
3.11.2 Standard tying
3.11.3 Comfort tying
3.11.4 Tying settings
3.11.5 Twine box (depending on equipment)
3.11.6 Spare net storage (depending on equipment)
3.11.7 Net box (depending on equipment)
3.12 Bale discharge
3.12.1 Bale ramp
Use without the bale ramp
3.13 Lubricating oil system
3.13.1 Automatic chain lubrication
3.14 Greasing system
3.14.1 General points
3.14.2 Manual central lubrication (optional)
3.14.3 Automatic central lubrication (optional)
3.14.4 Automatic central electric lubrication (optional)
3.15 Brake
3.15.1 General points
3.15.2 Hydraulic brakes
3.15.3 Active hydraulic brakes
3.15.4 Pneumatic brakes
3.16 Hydraulic system
3.16.1 Baler hydraulic unit
3.16.2 Continuous hydraulic circulation
3.17 Equipment
3.17.1 Ladder (Depending on equipment)
3.17.2 Step
3.17.3 Pressure gauge
3.17.4 Electronic module
4 Operating and control elements
4.1 OPERATOR
4.1.1 Presentation
4.1.2 Description of the OPERATOR menus
4.2 COMMUNICATOR II
4.2.1 Presentation
4.2.2 Description of the COMMUNICATOR Use menus
4.3 ISOBUS terminal
4.3.1 General points
4.4 EASY on board
4.4.1 Presentation
4.4.2 General points
5 Technical specifications
5.1 Baler
5.1.1 Dimensions
5.1.2 Weight
5.1.3 Hitching
5.1.4 Universal drive shaft
5.1.5 Feeding and baling
5.1.6 Tying device
5.1.7 Wheels
5.1.8 Hydraulic circuit
5.1.9 Bolt tightening torques
5.1.10 Braking
5.1.11 Greasing and lubrication
5.1.12 Noise level
5.2 Safety devices
5.2.1 Shear bolt
5.2.2 Torque limiter
5.3 Tractor
5.3.1 Power required
5.3.2 Hitching
5.3.3 Power take-off
5.3.4 Electrical connections
5.3.5 Hydraulic connections
5.3.6 Hydraulic oil and circuit
5.3.7 Braking
6 Machine preparation
6.1 General information
6.1.1 Before first use
6.1.2 Checking the equipment
6.2 Universal drive shaft
6.2.1 Safety advice
6.2.2 Overlap of the universal drive shaft
6.2.3 Adapting the length of the universal drive shaft
6.2.4 Conversion kit – 8 splines*
6.2.5 Fitting the universal drive shaft
6.3 Coupling frame
6.3.1 Recommendations
6.3.2 Coupling types
6.3.3 Adapting jaw drawbar/swinging drawbar
6.3.4 Fitting the universal drive shaft
6.3.5 Retaining cable (machine not equipped with brake and which can be used in France)
6.4 Hydraulic connections
6.4.1 With OPERATOR*
6.4.2 With COMMUNICATOR*
6.5 Electrical connections
6.5.1 Identifying the electrical cables
6.5.2 Lighting
6.5.3 Battery cable (optional)
6.5.4 Power supply for the baler and the OPERATOR*
6.5.5 Power supply for the baler and the COMMUNICATOR*
6.5.6 Power supply for the baler using the ISOBUS cable
6.5.7 Baler power supply with
6.6 Brake
6.6.1 Hydraulic brakes
6.6.2 Active hydraulic brakes
6.6.3 Pneumatic brake
6.7 Twine tying
6.7.1 Twine quality
6.7.2 Preparation
6.7.3 Adjusting the twine tensioner
6.7.4 Fitting the twine
6.7.5 Fitting the side stop for the twine
6.7.6 Selecting standard twine tying*
6.7.7 Selecting comfort twine tying*
6.8 Net tying
6.8.1 Preparation
6.8.2 Fitting the net
6.8.3 Adjusting the net brake
6.8.4 Selecting standard net tying*
6.8.5 Selecting comfort net tying*
6.9 Bale discharge
6.9.1 Fitting the bale ramp
6.9.2 Pre-setting the bale ramp
6.10 Baling chamber
6.10.1 Bale starting stops
6.10.2 Setting the MPS
6.11 Cutting unit
6.11.1 Safety advice
6.11.2 Checking
6.11.3 Fitting the knives
RotoCut baler with fixed rotor floor*
RotoCut baler with pivoting rotor floor*
6.11.4 Fitting the dummy knives*
6.11.5 Unused knives and dummy knives
6.12 Loading the machine
6.12.1 Lashing the baler
6.12.2 Lifting points
6.12.3 Lifting
7 Operation
7.1 General information
7.1.1 Baler user
7.1.2 Side doors
7.2 Travelling with the baler
7.2.1 Checking the equipment
7.2.2 Preparing for transportation
7.2.3 Travelling on the road
7.2.4 Arriving at the field
7.2.5 Driving in fields
7.2.6 Parking
7.3 Before each usage
7.3.1 Universal drive shaft
7.3.2 Reminders
7.3.3 Baler maintenance
7.3.4 Checking the equipment
7.4 Commissioning in the field
7.4.1 User advice
7.4.2 Starting the machine
Machine equipped with OPERATOR*
Baling pressure
Universal drive shaft
Cutting system
Stopping
Machine equipped with COMMUNICATOR* or an ISOBUS* connection
Continuous hydraulic circulation
Baling pressure
Universal drive shaft
Cutting system
Stopping
7.5 Pick-up
7.5.1 Important
7.5.2 Pick-up wheels
7.5.3 Pick-up height
7.5.4 Crop guard
7.6 Tying
7.6.1 Selecting twine or net tying (optional)
7.6.2 Setting the number of twine wraps
Machine equipped with standard tying
Reminder
Setting system
Tying drive belt positions
Setting the number of twine wraps
Tying drive pulley positions
Changing the pulley position
Machine equipped with comfort tying
Reminder
7.6.3 Setting the number of net wraps
Machine equipped with standard tying
Reminder
Setting system
Position of the eccentric stop
Setting the number of wraps
Machine equipped with comfort tying
Reminder
7.6.4 Replacing the net roller
Standard tying*
Comfort tying*
7.7 Bale parameters
7.7.1 Bale settings
7.8 OPERATOR
7.8.1 Counters Menu
7.8.2 Bale parameter settings
Tying delay
Setting the tying delays
Selecting the tying type
7.8.3 Baling/tying process
7.8.4 Manually activating the tying process
7.8.5 Manually delaying the tying process
7.8.6 RotoCut with fixed rotor floor*
7.8.7 RotoCut with pivoting rotor floor*
7.8.8 Faults
7.9 COMMUNICATOR II
7.9.1 Counters Menu
Resetting the maintenance indicator
Maintenance indicator
Resetting
7.9.2 Choice of job
7.9.3 Job name
7.9.4 Printing the customer or job data
7.9.5 Settings Menu
Setting the usage parameters
Settings
Selecting the tying type
Number of net or twine wraps*
Tying delay
Automatic knife cleaning
Automatic pressure recharge
Automatic tailgate opening
Interval between 2 lubrication operations (electric central lubrication*)
7.9.6 Pick-up
7.9.7 Pressure recharge
7.9.8 Opening the tailgate
Manual tailgate opening/closing
Manual tailgate opening
Manual tailgate closing
Softkeys
7.9.9 RotoCut cutting unit*
7.9.10 Pivoting rotor floor*
7.9.11 Manually activating the tying process
Anticipated tying start
Tying delay
Softkeys
7.9.12 Baling/tying process
Baling/tying process steps
Comfort net tying steps
Comfort twine tying steps
7.9.13 Electric central lubrication*
7.9.14 Faults
7.9.15 Functions which can be assigned to softkeys
7.10 ISOBUS terminal
7.10.1 General points
7.11 EASY on board
7.11.1 General points
7.12 Unblocking the baler
7.12.1 How can blockages be avoided?
7.12.2 Safety advice
7.12.3 Unblocking the pick-up
7.12.4 Unblocking the rotor (baler equipped with OPERATOR)
7.12.5 Unblocking the rotor (baler equipped with COMMUNICATOR)
7.13 After use
7.13.1 Reminders
7.13.2 Securing the baler
7.13.3 Daily cleaning
7.13.4 Unhitching the baler
8 Faults and remedies
8.1 General information
8.1.1 Sensors
8.2 OPERATOR
8.2.1 Bale discharge
8.2.2 Twine tying*
8.3 COMMUNICATOR II
8.3.1 General points
8.3.2 Bale discharge
8.3.3 Net tying
8.3.4 Twine tying
8.3.5 Cutting floor
8.4 Tying system
8.4.1 Cause of the faults
8.4.2 Net tying
8.4.3 Twine tying
8.5 Lubricating oil system
8.5.1 Cause of the problems
8.5.2 Resolving faults
8.6 Greasing system
8.6.1 Central lubrication
8.7 Other functions
8.7.1 General points
8.7.2 General functions
9 Maintenance
9.1 General maintenance information
9.1.1 Maintenance and safety advice
9.1.2 Wheels and tyres
9.1.3 Brakes
9.1.4 Hydraulic circuit
9.1.5 V-belt
9.1.6 Chains
9.1.7 Baling/tying device
9.1.8 Hitching
9.1.9 Universal drive shaft
9.1.10 Cutting unit
9.1.11 Safety device
9.1.12 Nuts and bolts
9.1.13 Lubricants and lubricating
9.1.14 Inductive sensors
9.1.15 Welding work
9.1.16 Replacement parts
9.2 Maintenance schedules
9.2.1 Maintenance operations before gathering crop
9.2.2 Maintenance operations after the first 10 hours of operation
9.2.3 Maintenance operations after the first 50 hours of operation
9.2.4 Maintenance operations every 8 hours of operation or every day
9.2.5 Maintenance operations every 50 hours of operation
9.2.6 Maintenance operations every 100 hours of operation
9.2.7 Maintenance operations every 250 hours of operation
9.2.8 Maintenance operations, annual or every 500 hours of operation
9.2.9 Maintenance operations if necessary
9.3 Lubricants charts
9.3.1 Lubricants
9.4 Lubrication plan
9.4.1 Lubrication
9.4.2 Lubrication points – 8 h
9.4.3 Lubrication points – 50 hrs
9.4.4 Lubrication points – 100 h
9.4.5 Lubrication points – 250 h
9.5 Maintenance operations gearbox
9.5.1 540 rpm drive gearbox
9.5.2 1000 rpm drive gearbox
9.5.3 Universal drive shaft shear bolt
Replacing the bolt
9.6 Maintenance operations axle and wheels
9.6.1 Checking the tyres
9.6.2 Checking the wheel tightness
9.6.3 Changing the wheels
9.6.4 Wheel hub
9.7 Maintenance operations brake
9.7.1 Hydraulic brakes and active hydraulic brakes
9.7.2 Pneumatic brakes
9.7.3 Replacing the brake pads
9.8 Maintenance operations hitch
9.8.1 Hitch coupling and drawbar mounting
9.9 Maintenance operations hydraulic system
9.9.1 Filter
9.10 Maintenance operations pick-up
9.10.1 Pick-up drive chains
9.10.2 Pick-up shear bolt
9.10.3 Pick-up tensioner
9.11 Maintenance operations feeder unit
9.11.1 Rotor drive spring
9.11.2 Setting the knife height (RotoCut Machines)
9.12 Maintenance operations baling chamber
9.12.1 MPS springs (oscillating segment)
9.12.2 Roller drive springs
9.12.3 Cleaning the roller
9.13 Maintenance operations tying
9.13.1 Twine tying
9.13.2 Net tying
9.14 Maintenance operations bale discharge
9.14.1 Bale ramp
9.15 Maintenance operations lubrication system
9.15.1 Chain lubrication
9.16 Maintenance operations greasing system
9.16.1 Manual lubrication
9.16.2 Manual central lubrication of the bearings (optional)
9.16.3 Automatic central lubrication of the bearings (optional)
9.16.4 Automatic electric central lubrication (option)
9.17 Maintenance operations machine body
9.17.1 Extinguisher (optional)
9.18 Winter storage
9.18.1 General points
9.18.2 Cleaning
9.18.3 Lubricating
9.18.4 Maintenance
9.18.5 Storage
10 Placing out of operation and disposal
10.1 General information
10.1.1 Placing out of operation and disposal
11 EC declaration of conformity
11.1 General information
11.1.1 Declaration of Conformity for EC
00 2348 408 0.pdf:
CEMIS 100
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 General information
1.1.1 Validity of the manual
1.1.2 Information about this Operator’s Manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Intended use
1.2.2 Reasonably foreseeable misuse
2 Safety
2.1 Safety rules
2.1.1 General safety and accident prevention regulations
2.1.2 Interaction between terminal and machine or tractor
2.1.3 Electrocution by electrical system
3 Product description
3.1 Overview and method of operation
3.1.1 Overview of CEMIS 100
3.1.2 Function principle of CEMIS 100
3.2 Identification plates and identification numbers
3.2.1 Spare parts and technical questions
3.2.2 Identification plate of CEMIS 100
4 Operating and display elements
4.1 CEMIS 100
4.1.1 User interface for LINER
4.1.2 User interface for ROLLANT
4.1.3 User interface for UNIWRAP
5 Technical specifications
5.1 CEMIS 100
5.1.1 Specification
6 Operation
6.1 CEMIS 100
6.1.1 Operating the CEMIS 100
6.1.2 Switching CEMIS 100 on
6.1.3 Switching CEMIS 100 off
7 Maintenance
7.1 CEMIS 100
7.1.1 Daily
8 Putting out of operation and disposal
8.1 General information
8.1.1 Removal from service and disposal
9 Technical terms and abbreviations
9.1 Terms and explanations
9.1.1 Technical words
9.1.2 Abbreviations
00 2348 427 0.pdf:
CEMIS 700
Table of contents
1 Introduction
1.1 General information
1.1.1 Validity of the manual
1.1.2 Information about this Operator’s Manual
1.1.3 Symbols and notes
1.2 Intended use
1.2.1 Intended use
1.2.2 Reasonably foreseeable misuse
2 Safety
2.1 Safety rules
2.1.1 General safety and accident prevention regulations
2.1.2 Interaction between terminal and machine or tractor
2.1.3 Electrocution by electrical system
3 Product description
3.1 Overview and method of operation
3.1.1 Overview of CEMIS 700
3.1.2 Function principle of CEMIS 700
3.2 Identification plates and identification numbers
3.2.1 Spare parts and technical questions
3.2.2 Identification plate of CEMIS 700
4 Information on the product
4.1 Software version
5 Operating and display elements
5.1 CEMIS 700
5.1.1 User interface
5.1.2 Terminal program
6 Technical specifications
6.1 CEMIS 700
6.1.1 Specification
7 Operation
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Parts Catalog PDF
John Deere Tractors 7500 Parts Catalog CPCQ26568 30 Jan 02 Portuguese
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere PowerTech M 10.5 L and 12.5 L Diesel Engines COMPONENT TECHNICAL MANUAL CTM100 10MAY11
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere DF Series 150 and 250 Transmissions (ANALOG) Component Technical Manual CTM147 05JUN98
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Repair Technical Manual PDF
John Deere Transmission Control Unit Component Technical Manual CTM157 15JUL05